Source



![]() Source is a 3D game engine created by
Source is a 3D game engine created by ![]() Valve in 2004, and is the successor to
Valve in 2004, and is the successor to ![]() GoldSrc. The Source engine is well-known for its advancements in physics, AI, and graphics which made the game realistic for it's time, while being scalable on older, less powerful hardware. One game,
GoldSrc. The Source engine is well-known for its advancements in physics, AI, and graphics which made the game realistic for it's time, while being scalable on older, less powerful hardware. One game, ![]() Half-Life 2, earned several awards for it's graphics, which were made possible with Source. Source has been used by Valve, third-party companies, and (much like GoldSrc) countless community mods by people around the globe, with at least 100 games developed on Source. Despite the Source engine being almost 20 years old, and has been superseded by the
Half-Life 2, earned several awards for it's graphics, which were made possible with Source. Source has been used by Valve, third-party companies, and (much like GoldSrc) countless community mods by people around the globe, with at least 100 games developed on Source. Despite the Source engine being almost 20 years old, and has been superseded by the ![]() Source 2 engine for first-party usage since 2015, it's still being commonly used today by modders and some third-party companies due to the lack of some Source 2 documentation and was rarely licensed to third-party developers compared to Source, and it's still regularly being maintained with engine and security updates.
Source 2 engine for first-party usage since 2015, it's still being commonly used today by modders and some third-party companies due to the lack of some Source 2 documentation and was rarely licensed to third-party developers compared to Source, and it's still regularly being maintained with engine and security updates.
Renderer
- Version 3.0 (and below) shaders
- Anti-aliasing support
- Source is the first Valve engine to support anti-aliasing, prior to MSAA (4X) being added to GoldSrc in 2013.
- MSAA is the traditional anti-aliasing method, works by samples (renders) each pixel multiple times at different locations within the frame and averages the samples to produce the final pixel value. It is commonly used in most older video games, including almost all Source engine games (except
 Black Mesa (since the Xen update),
Black Mesa (since the Xen update),  Apex Legends, etc...). Up to 8x MSAA (or 6x MSAA in Source 2004) is supported. Older GPUs (such as pre-Maxwell Nvidia cards) also support CSAA.
Apex Legends, etc...). Up to 8x MSAA (or 6x MSAA in Source 2004) is supported. Older GPUs (such as pre-Maxwell Nvidia cards) also support CSAA. - FXAA is also supported in CS:GO engine branch. Unlike MSAA, FXAA has less performance hit than most other AA methods due to it being a post-processing effect, which meant that it can be unofficially added to older Source engine games (or even other video games, other engines and other applications in general), using software such as ReShade, or even built-in via the graphics driver settings, and unlike MSAA, FXAA and other post-processing method will affect transparent textures, however, due to it's nature, this makes FXAA looks worse than many other AA methods as it's appear to blur the image, plus it does not reconstruct the pixel which was missing due to lack of an traditional anti-aliasing.
- MLAA is another post-processing anti-aliasing method, which is used in
 PlayStation 3 version of
PlayStation 3 version of  Portal 2. MLAA has a larger performance impact than FXAA.
Portal 2. MLAA has a larger performance impact than FXAA. Confirm:What about anti-aliasing on the PS3 version of CS:GO?
Confirm:What about anti-aliasing on the PS3 version of CS:GO? - TAA is a modern AA method commonly used in most modern games, superseded the MSAA method for anti-aliasing, it works by combining information from past frames and the current frame to remove jaggies in the current frame. However, as mentioned, TAA combines information from past and current frames can cause blurring and ghosting effect while in motion, more noticeable with low FPS. In Source engine case, it is only available in few games such as
 Apex Legends.
Apex Legends. Tip:If the game is running in 4K resolution or above, or by downscaling 4K to 1080p or lower, the need for anti-aliasing is greatly reduced.
Tip:If the game is running in 4K resolution or above, or by downscaling 4K to 1080p or lower, the need for anti-aliasing is greatly reduced.
- More anisotropic and texture filtering options
- Anisotropic filtering allow textures on far distance to look sharper and less blurry.
- Compared to GoldSrc (prior to 2013) featuring only Bilinear or Trilinear texture filtering, Source features more texture filtering options, ranging from Bilinear, Trilinear, 2x Anisotropic to 16x.
- Bump mapping and Normal mapping on models and the world
- Author shaders with HLSL
- Cube and environment mapping
- Cubemapping also supports Anisotropy (in all games since
 )
)
- Cubemapping also supports Anisotropy (in all games since
- Phong shading for models
- Phong is also supported on world brushes (in all games since
 )(also in
)(also in  )
)
- Phong is also supported on world brushes (in all games since
- Dynamic lights, vertex lighting and lightmaps, many light types including flickering, pulsing etc.
- HDR (in all games since
 ) and SDR/LDR (not in
) and SDR/LDR (not in  and later) (except
and later) (except  Dota 2 (pre-Reborn)) lighting
Dota 2 (pre-Reborn)) lighting - Water with refraction, real-time world reflections and fresnel effects
- Water also supports flow mapping (in all games since
 )
)
- Water also supports flow mapping (in all games since
- Advanced particle systems that can emit sprites or models
- Render-to-texture shadows allow for a large number of characters per scene (in all games since
 ) (also in
) (also in 
 )
) - Occluder entities for visibility blocking
- Indoor/Outdoor environments
- Deformable terrain
- 3D Skyboxes extend the horizon and add parallax on distant objects
- Dynamically rendered organics (grass, trees, etc.)
- Swaying trees (in all games since
 ) (also in
) (also in 


 )
)
- Subdivision surfaces, diffuse & specular bump maps
- Real-time radiosity lighting
- Real-time Cascaded Shadow Mapping that comes from the skybox (in all games since
 ) (also in
) (also in 
 )
) - Effects include but are not limited to: particles, beams, volumetric smoke, sparks, blood, & environmental effects like fog and rain
- Scalability
- Widescreen display support
- Source is one of the earliest game engines to support Widescreen monitors natively (16:9 and 16:10 aspect ratio) without stretching the image, while most games from that era are usually designed for 4:3/5:4 displays only. Games such as
 Half-Life 2 support widescreen display at launch back in 2004, with horizontal FOV (field of view), allow you to see more details.
Half-Life 2 support widescreen display at launch back in 2004, with horizontal FOV (field of view), allow you to see more details.
- Source is one of the earliest game engines to support Widescreen monitors natively (16:9 and 16:10 aspect ratio) without stretching the image, while most games from that era are usually designed for 4:3/5:4 displays only. Games such as
- Physically Based Rendering (only in




 )
) - Parallax Occlusion Mapping(only in

 )
) - DirectX (Direct3D) Levels
 Note:Most Source engine games are usually runs on Direct3D 9 (or 11/12 in some third-party games), but some features (such as shaders) may not be available on older cards that was designed for previous DirectX versions.
Note:Most Source engine games are usually runs on Direct3D 9 (or 11/12 in some third-party games), but some features (such as shaders) may not be available on older cards that was designed for previous DirectX versions.- DX6(only in
 )(not in
)(not in  and later)
and later) - DX7(only in


 )(not in
)(not in  and later)
and later) - DX8 and DX8.1 (only in
 to
to  )(not in
)(not in  and later)
and later) - DX9(only in
 to
to  )(not in
)(not in  and later)
and later) - DX9.0c(in all games since
 )
) - DX9.8(in all games since
 ) which is only on the Xbox 360
) which is only on the Xbox 360 - DX9Ex(in all games since
 ) (also in
) (also in  ) - DX9 Windows Aero extension, requires Vista or later. User can enable/disable in Video Settings - Advanced (Windows Aero extensions), or through
) - DX9 Windows Aero extension, requires Vista or later. User can enable/disable in Video Settings - Advanced (Windows Aero extensions), or through -disable_d3d9ex(only in ).
). - DX10(only in
 SFM,
SFM,  Dota 2 (pre-Reborn))
Dota 2 (pre-Reborn)) - DX11(only in


 )
) - DX12(only in
 )
)
-dx9, if it was forced by commands such as -gamepadui, which enables both the Gamepad UI and Vulkan renderer unless combined with -dx9-eac_launcher_settings SettingsDX12.json- OpenGL(in all games since
 /
/ ) which is a graphics API that replaces DirectX for macOS and Linux.
) which is a graphics API that replaces DirectX for macOS and Linux.
- Vulkan which is a graphics API that replaces DirectX or OpenGL (only in





 )
)
-vulkanMaterials System
- Instead of traditional textures, Source defines sets of materials that specify what the object is made from and the texture used for that object. A material specifies how an object will fracture when broken, what it will sound like when broken or dragged across another surface, and what that object's mass and buoyancy are. This system is much more flexible than other texture-only systems
- Materials can interact with objects or NPCs, such as mud or ice for vehicles to slide/lose traction on
Multiplayer Network Code
- Time- and gamer-tested by millions of gamers around the world
- Support for both LAN-based multiplayer and Internet-based multiplayer games
- Prediction analysis for interpolating collision/hit detection
- Optimizations for high-latency, high-packet-loss 56k connections
Advanced Characters
- Detailed and believable characters
- Realistic eyes
- Focus on player/object, not simply parallel views
- Proper eye bulge for realistic eye reflections
- Simulated musculature provides outstanding emotions, speech, and body language
- Language independent speech, characters can speak naturally in many languages
- Skeletal/bone system for animation
- Layered animation system can synthesize complex animations out of several pieces
Physics
- Uses Havok physics engine, licensed from Havok Group (now acquired by Microsoft)
- More responsive world with realistic interactions
- Sounds & graphics follow from physics
- AI characters can interact with physically simulated objects
- Ropes/cables, machines, constraint systems, ragdoll physics
- Can be controlled by level design
- Kinematic animated bone followers
- Custom procedural physics controllers
- Vehicles
- Wheels slip and skid
- Realistic suspensions with springs on each wheel
- Realistic leaning during acceleration/deceleration and turning
- Individually tunable parameters such as horsepower, gearing, max speed, shift speed, tire material, tire friction, spring tension/dampening, etc.
- Multiple players in a vehicle in multiplayer
- Hovercraft support for cheaper simulation
Advanced AI
- I/O system allows level designers to control AI
- Sophisticated navigation: characters that run, fly, jump, crouch, climb stairs and ladders, and burrow underground
- AI senses things using sight, sound, and smell
- AI relationships determine friend/foe status of other entities
- Battle AI allows squads of AI characters to operate together, know when to advance, retreat, lay cover fire, etc.
Sound System
- 7.1, 5.1 surround sound, 4 speaker surround
 Bug:On system running Windows Vista and later, due to the game engine using DirectSound and older version of Miles Sound System, the game may output only 5.1 surround despite 7.1 selected or 7.1 audio may not work properly without custom
Bug:On system running Windows Vista and later, due to the game engine using DirectSound and older version of Miles Sound System, the game may output only 5.1 surround despite 7.1 selected or 7.1 audio may not work properly without custom dsound.dll(such as Creative Alchemy, DSOAL or IndirectSound). This issue is not affected by some third-party games, such as Titanfall 2,
Titanfall 2,  Apex Legends. [todo tested in ?]
Apex Legends. [todo tested in ?] Note:Some Source games (such as
Note:Some Source games (such as  Alien Swarm,
Alien Swarm,  Portal 2 and
Portal 2 and  Counter-Strike: Global Offensive) may not include options to enable 7.1 surround sound without using console commands.
Counter-Strike: Global Offensive) may not include options to enable 7.1 surround sound without using console commands.
- High-quality 3D spatialization
- Custom software DSP
- Automatic DSP based on environmental geometry
- Microsoft ADPCM-compressed WAV files
- 16-bit 44.1 KHz (CD Quality), stereo wave data with all features
 Warning:48 KHz audio (DVD Quality) is not supported by default. Not to be confused with 44.1 KHz, which is the CD Quality audio.
Warning:48 KHz audio (DVD Quality) is not supported by default. Not to be confused with 44.1 KHz, which is the CD Quality audio.
- MP3 decompression (requires Miles license)
- Support for audio streaming on any wave [Clarify]
- Real-time wave file stitching [Clarify]
- Pre-authored Doppler effect encoded waves
- Pre-authored distance variant encoded waves
- Commentary system
UI
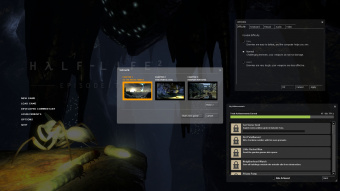

- Server browser — Displays all active game servers and allows a player to choose which one to participate in. Players can filter and sort server lists to speed up the display and selection of a server.
- VGUI — Valve's custom GUI interface mimics most of the Windows controls but is rendered using the Source engine for both in game and out of game uniform UI display. Some features:
- Dynamic in-game HUD display
- Many widgets/controls (e.g., buttons, treeview, html control…)
- Themes/custom visualization allowed
- Platform independent
- Localized text (Unicode compliant)
- Gamepad UI (
 Source 2013 version) — Since the release of
Source 2013 version) — Since the release of  Half-Life 2 (and its episodes) as well as
Half-Life 2 (and its episodes) as well as  Portal updates in 2022, Valve have added a modern UI which is designed for consoles and handhelds like
Portal updates in 2022, Valve have added a modern UI which is designed for consoles and handhelds like  Steam Deck. With the new Gamepad UI, it was more scalable across any resolution (including 4K and higher), unlike the regular VGUI (which, the higher the resolution, the text and UI will become smaller). This UI can be also enabled manually by using
Steam Deck. With the new Gamepad UI, it was more scalable across any resolution (including 4K and higher), unlike the regular VGUI (which, the higher the resolution, the text and UI will become smaller). This UI can be also enabled manually by using -gamepaduicommand line argument (which will also enable Vulkan renderer that may not work on some older GPUs unless-dx9is used in combination of-gamepadui).
- Scaleform (officially called Scaleform GFx) — Introduced with
 CS:GO engine branch at launch until 2018, this is a vector graphics rendering engine used to display
CS:GO engine branch at launch until 2018, this is a vector graphics rendering engine used to display  Adobe Flash-based UI and HUD for games.
Adobe Flash-based UI and HUD for games. - Panorama (in all games since
 ) — Introduced in 2018, replacing Scaleform, Valve's new Custom GUI interface that resembles modern web design and authoring (HTML5/CSS/JS). Using
) — Introduced in 2018, replacing Scaleform, Valve's new Custom GUI interface that resembles modern web design and authoring (HTML5/CSS/JS). Using .XMLand JavaScript files, developers can create dynamic and clean HUDs and menus and even high-quality in-game intractable panels.
Programming
- Source natively support various CPU architectures, such as x86 (PC and 8th, 9th-gen Consoles), ARM (
 Android,
Android,  Nintendo Switch), PowerPC (
Nintendo Switch), PowerPC ( Xbox 360,
Xbox 360,  PlayStation 3), and more, with both 32 and 64-bit.
PlayStation 3), and more, with both 32 and 64-bit.
- Support for 64-bit architecture will allow Source to handle more than 2-4GB of RAM limit.
- Historically,
 Half-Life 2 had a 64-bit update in 2005, but it was later removed for unknown reasons.
Half-Life 2 had a 64-bit update in 2005, but it was later removed for unknown reasons.  CS:GO later received an 64-bit update in 2016 for Mac and Linux systems. On April 19, 2024,
CS:GO later received an 64-bit update in 2016 for Mac and Linux systems. On April 19, 2024,  Team Fortress 2 was upgraded to 64-bit on Windows and Linux.
Team Fortress 2 was upgraded to 64-bit on Windows and Linux.
- All code written in C/C++ using Visual Studio .NET 2003 and later. Easily and quickly derive new entities from existing base classes
- Internal context sensitive performance monitoring system
- Graphics performance measurement tools built into the engine
- Modular code design (via DLLs) allows swapping out of core components for easy upgrading or code replacement
- VScript scripting system allows using external coding languages, such as Squirrel and Lua, in maps to create more complex systems (in all games since
 ) (also in
) (also in 
 )
)
Tools
 HLFaceposer
HLFaceposer
- Facial expression tool used to craft speech and emotions
 Valve Hammer Editor
Valve Hammer Editor
- WYSIWYG World editor
- Create world brushes
- Terrain editor
- Place detailed world models and AI NPCs
- Set navigation points/paths for NPCs
- Place triggers, clip brushes, logic, etc.
- Allows level designer to hook up I/O between entities to control AI within the game
 Half-Life Model Viewer
Half-Life Model Viewer
- Full model previewer
- Rotate models in any direction
- Set up hit boxes
- View physics hull
- View normals
- Wireframe, shaded or textured view modes
- Studiomdl
- Model compiler
- VBSP, VRAD, VVIS, VMPI
- Map compilation tools (bsp, lighting and visibility)
- VMPI — distributed compilation tool allowing level compiles to be spread across many PCs greatly reducing compile times
- Exporters
- XSI, Max and Maya
.smdexporters for exporting 3D models
- XSI, Max and Maya
Products using Source 

This is the list of games that uses the ![]() Source engine.
Source engine.
Products made by Valve
| Release date | Title | Co-developed with | Engine branch | Platforms | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Oct 2004 | |
Turtle Rock Studios Hidden Path Entertainment (2010 update) |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | First game to use the Source engine. Remake of Counter-Strike. Hidden Path Entertainment alongside Valve worked on the May 7, 2010 update, which upgraded the game's engine from Source 2006 to 2009 (MP version, later renamed to Source MP), and added 144 (now 146) achievements, a new domination and revenge system similar to Team Fortress 2, player stats and more. Hidden Path Entertainment also worked on the unreleased Xbox 360 port of CS:S, which would later become |
| 16 Nov 2004 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Remaster of Half-Life. It is critically panned by most gamers since 2013 due to the huge amount of bugs that were introduced when the game was updated to A unofficial fan remake of Half-Life, called Black Mesa was later started development in response of those criticisms, which was first released in 2012 without any Xen chapters and was much shorter, and later in 2020, a full release with contains the Xen chapters. |
|
| 16 Nov 2004 | |
EA UK (PS3 port) | |
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Original Xbox, Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 |
Sequel to Half-Life, and later Half-Life: Alyx. Included on The game was set 20 years after the event of Half-Life, takes place in City 17, which is under Combine control. Prior to its release, it was delayed multiple times, and infamously leaked in Oct 2003. It was among the first games to require Steam in order to play. Half-Life 2's engine branch has been updated multiple times, first in 2007, upgraded to Source 2007 only on consoles, and in 2010, upgraded to Source 2009 on PC, and finally, Half-Life 2 was upgraded to the Source 2013 Singleplayer branch. In November 2024, Valve released a 20th anniversary update, which add Steam Workshop support, fixing several bugs, improved shaders (with option to use classic 2004/2006 particles/effects and Very High shader option), and made Half-Life 2: Lost Coast, Episode One and Episode One playable through Half-Life 2 main menu, without quitting the game and launch it separately on Steam client. |
| 30 Nov 2004 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Multiplayer component of Half-Life 2. Now runs on Team Fortress 2 branch after 20th anniversary update. | |
| 26 Sep 2005 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Remake of Day of Defeat. Like Half-Life 2: Lost Coast, it also have features later added to Source 2006, such as HDR lighting. | |
| 27 Oct 2005 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Originally as part of Half-Life 2, which was cut at some point before it was released, and was developed after the leak happened but was ultimately cut, then later released in 2005 as a HDR lighting technology demo. It runs on a newer version of Source 2004, introducing new features such as Commentary System and HDR (which was previously introduced on Day of Defeat: Source). Both of these new features are later used in Half-Life 2: Episode One, which runs on Source 2006 engine, and subsequent games & branches after it. As of 2025, it runs on |
|
| 1 May 2006 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Multiplayer component of Half-Life: Source. Now runs on Team Fortress 2 branch since February 18, 2025 update. | |
| 1 Jun 2006 | |
EA UK (PS3 port) | |
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 |
The game is the sequel to Half-Life 2, and the story begins after the Citadel reactor core was destroyed, Gordon and Alyx both survived the explosion. When it's come to technical, it used the |
| 10 Oct 2007 | |
EA UK (PS3 port) | |
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 |
A sequel to Half-Life 2: Episode One. The City 17 has been destroyed, and the Citadel was partially collapsed, Gordon and Alyx has survived the train crash. The game largely take places in White Forest. Story aside, when it's come to technical, it uses the |
| |
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, Nintendo Switch (part of Portal Companion Collection) |
A completely new game and IP from Valve, set in the Half-Life universe, and take places in Aperture Laboratories. It is a puzzle-based shooter game, allowing you to create portals, that link to one another on any flat and large enough surface. In 2023, an unofficially remastered version of the game, Portal with RTX, was released, which takes advantage of hardware that support ray-tracing, and adds PBR textures, high polygon models in order to improve the game graphics. Like the other two new games in The Orange Box package, it used the |
|||
| |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 | Sequel to Team Fortress Classic, focusing on cartoon graphics unlike the pre-release footage/screenshots, which aimed to be more realistic. This is the last game, along with 2 other games as part of The Orange Box pack to use the engine branch that requires Half-Life 2 assets to operate. The console version of the game is no longer updated, as opposed to PC version of the game, which is frequently updated. It has its own version of Source 2013 Multiplayer which is more up to date and has newer features in what's named the Team Fortress 2 branch. |
||
| 17 Nov 2008 | |
Turtle Rock Studios (under Valve South) |
|
PC: Windows, Mac Console(s): Xbox 360 |
A new multiplayer co-op game, with a horror zombie theme. It use a new engine branch which does not require Half-Life 2 assets in order to work, it also adds many new features and introduced VPKs. |
| 17 Nov 2009 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360 |
Originally was planned to be an update for Left 4 Dead, it was later released as standalone game. Like Left 4 Dead, it also runs on the same L4D branch, but much newer. Like TF2, the console version ( This game was also ported to Source 2 back in 2014, but this version remains unreleased to this day, and one of its maps has been remade in Source 2 as a tech demo back in 2010, which its image was leaked in 2014. |
|
| 19 Jul 2010 | |
|
PC: Windows | A co-op alien shooter, which was a remake of the Unreal Tournament 2004 mod with the same name. It succeeded the |
|
| 18 Apr 2011 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, Nintendo Switch (part of Portal Companion Collection) |
Has its own engine branch, and once again, introduced new features and succeeded |
|
| 21 Aug 2012 | |
Hidden Path Entertainment | |
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux Console(s): Xbox 360, PlayStation 3 |
Sequel to Counter-Strike: Source, originally developed as a Xbox 360 port of Counter-Strike: Source before Valve eventually turned it into a new Counter-Strike game. The game runs on the CS:GO engine branch, which is based off of the Left 4 Dead engine branch with Portal 2 engine branch code. CS:GO used Source 1 engine until 2023, now uses the new Source 2 engine under the name Counter-Strike 2, replacing CS:GO (except the console version). Console version is no longer updated since 2013, but remains purchasable. Prior to being delisted, it was Free to Play on PC since 2018. |
| 9 Jul 2013 | |
|
PC: Windows, Mac, Linux | Sequel to 2003's Warcraft III mod, Defense of the Ancients (retroactively called as Dota 1, DotA for short). Formerly using Source until 2015, when Dota 2 was ported to Source 2, as part of Dota 2's Reborn update. This is the last Valve game to be released on the Source engine. |
Third-Party
Games, tool and mods made by third-party companies and mod teams.
Released
|
|
|
In development (Unreleased)
This section are for unreleased third-party games and tools that have been announced, and it is currently in development, not publicly released, is in Beta/Early Access, or planned to be released.
|
More Third-party Source Engine games
See also
- Wikipedia:Source (game engine)
- Source Engine Features
- Source SDK
- Source SDK Documentation
- Source SDK 2013
External links
- Source Engine Tutorials https://www.sourcemodding.com/tutorials/source
- Tutorials for Source Engine https://gamebanana.com/tuts/games/35
- Tutorials - Source - Mod DB https://www.moddb.com/engines/source/tutorials
- GitHub Issues page - for engine bug reports.