VVIS: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
 Tip:For
Tip:For  TF2 branch games and
TF2 branch games and  Garry's Mod,
Garry's Mod,  VVIS++ is now available, which generates the same results as stock VVIS but at an order of magnitude quicker speed.
VVIS++ is now available, which generates the same results as stock VVIS but at an order of magnitude quicker speed.
(fast mode) |
No edit summary |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{LanguageBar}} | |||
{{Source topicon}} | |||
{{toc-right}} | |||
{{map compile pipeline|source1}} | |||
{{vvis|4}} is the [[command-line]] tool that takes a compiled [[BSP]] map and embeds visibility data into it. VVIS tests which [[visleaf|visleaves]] can see each other and which cannot. See [[Visibility optimization]] for a more detailed explanation. | |||
VVIS will: | |||
* Test visibility between [[visleaf|visleaves]] by [http://www.gdcvault.com/play/1014234/Excerpt-Quake-Postmortem-Optimizing-Level clipping their view planes]. | |||
* Enforce a maximum visibility distance, if configured to. | |||
{{tip|For {{tf2branch|nt=0|4.1}} games and {{gmod|2}}, {{vvis++|2}} is now available, which generates the same results as stock VVIS but at an ''order of magnitude'' quicker speed. | |||
Additionally, you can set up VVIS++ to work with [[VVIS++#Other games/mods tested|unofficially supported games]], such as {{hl2|1}}, {{portal|1}} and {{src13sp|1}} branch games. | |||
}} | |||
== Syntax == | |||
vvis [options...] <bsp file> | |||
For example: | |||
"Half-Life 2\bin\vvis.exe" -tmpout sdk_trainstation_01 | |||
This will generate and embed a visibility chart, writing portal data out to <code>.\tmp\sdk_trainstation_01.prt</code>. | |||
==Options== | ==Options== | ||
Use these in combination with [[expert compile mode]] or a batch file: | |||
=== Functions === | |||
; <code>-fast</code> | |||
: Only do a quick first pass. Does not actually test visibility. | |||
; <code>-radius_override <[[int]]></code> | |||
: Force a maximum vis radius, in [[unit]]s, regardless of whether an [[env_fog_controller]] specifies one. | |||
; <code>-nosort</code> | |||
: Don't sort (an optimization) portals. | |||
; <code>-tmpin</code> | |||
: Read portals from <code>\tmp\<mapname></code>. | |||
; <code>-tmpout</code> | |||
: Write portals to <code>\tmp\<mapname></code>. | |||
; <code>-trace <start cluster> <end cluster></code> {{source_2007|since}} | |||
: Writes a linefile that traces the vis from one cluster to another for debugging map vis. | |||
=== General === | |||
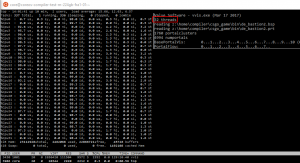
[[File:32cores16threads.png|300px|thumbnail|right|32 vCore machine running VVIS with only 16 cores used (even though 32 threads were specified)]] | |||
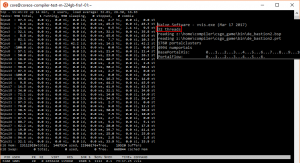
[[File:32cores32threads.png|300px|thumbnail|right|32 vCore machine running VVIS with all cores used (patched vvis used)]] | |||
; <code>-low</code> | |||
: Run as an idle-priority process. | |||
; <code>-threads</code> | |||
: Override the number of CPU threads used. Maximum is 16 threads (32 in {{csgo}}{{slamminsrc}}{{mapbase}}, unlimited in {{tf2}}) | |||
:{{Workaround|With a [[Increased_Thread_Limit_for_Compile_Tools|patched vrad_dll]] you can use 32 threads. {{l4d2}} [https://github.com/ficool2/fixtoolthreads fixtoolthreads] is a patch for [[VVIS]] (and [[VRAD]]) that supports ''unlimited'' threads and fixes a thread scaling issue.}} | |||
::{{Note|The above mentioned thread scaling issue has been fixed in {{tf2}},{{csgo}},{{l4d2}},{{gmod}}.}} | |||
:{{Tip|If you know that the compile time will be very long and would rather do something else while waiting, it may be useful to specify a number of threads 1 or 2 lower than what your CPU has. This allows the computer to allocate some more power to other applications, making it less choppy while lighting is being compiled. Keep in mind that this may slightly extend your compile time.}} | |||
; <code>-verbose (-v)</code> | |||
: Turn on verbose output | |||
; <code>-novconfig</code> | |||
: Don't bring up graphical UI on vproject errors. | |||
; <code>-mpi</code> | |||
: Use [[VMPI]] to distribute computations. | |||
; <code>-mpi_pw <[[string]]></code> | |||
: Use a password to choose a specific set of VMPI workers. | |||
; <code>-vproject <string></code> | |||
; <code>-game <string></code> | |||
: Override the [[VPROJECT]] environment variable. | |||
== Console Output == | |||
VVIS prints various information about the compile process to the console. Note that output from older versions of the tool can be different. | |||
; <code>''number'' portalclusters</code> | |||
: The effective number of visleaves in the map (visleaves clustered together with {{Ent|func_viscluster}} count as one). | |||
; <code>''number'' numportals</code> | |||
: The number of portals connecting the the above visleaves. | |||
; <code>BasePortalVis: 0...1...2...3...4...5...6...7...8...9...10 (''time taken in seconds'')</code> | |||
: Rough visibility calculations that are used to trivially weed out unseen areas from the final calculations. | |||
; <code>PortalFlow: 0...1...2...3...4...5...6...7...8...9...10 (''time taken in seconds'')</code> | |||
: Runs the actual visibility algorithm to determine which visleaves can see each other. Not run with <code>-fast</code>. | |||
; <code>Optimized: ''number'' visible clusters (''percentage'')</code> | |||
: Compression of the visibility data. | |||
; <code>Total clusters visible: ''number''</code> | |||
: The total number of occurrences of visleaves being able to see each other in the calculated data. | |||
; <code>Average clusters visible: ''number''</code> | |||
: The average number of leaves you can potentially see from each visleaf. | |||
; <code>Building PAS...</code> | |||
: Calculates the Potentially Audible Set. | |||
; <code>Average clusters audible: ''number''</code> | |||
: The average number of leaves you can potentially hear into from each visleaf. | |||
; <code>visdatasize: ''number'' compressed from ''number''</code> | |||
: Size of the visibility data in bytes. Max size is 16 MB in Source 2013. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[PRT]] | |||
* [[Visibility optimization]] | |||
{{sdktools}} | |||
[[Category:Official Source Tools]] | |||
[[Category:Source 1 BSP compilers]] | |||
[[Category:Tools]] [[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 00:38, 9 October 2025
![]() VVIS is the command-line tool that takes a compiled BSP map and embeds visibility data into it. VVIS tests which visleaves can see each other and which cannot. See Visibility optimization for a more detailed explanation.
VVIS is the command-line tool that takes a compiled BSP map and embeds visibility data into it. VVIS tests which visleaves can see each other and which cannot. See Visibility optimization for a more detailed explanation.
VVIS will:
- Test visibility between visleaves by clipping their view planes.
- Enforce a maximum visibility distance, if configured to.
Additionally, you can set up VVIS++ to work with unofficially supported games, such as Half-Life 2, Portal and Source 2013 Singleplayer branch games.
Syntax
vvis [options...] <bsp file>
For example:
"Half-Life 2\bin\vvis.exe" -tmpout sdk_trainstation_01
This will generate and embed a visibility chart, writing portal data out to .\tmp\sdk_trainstation_01.prt.
Options
Use these in combination with expert compile mode or a batch file:
Functions
-fast- Only do a quick first pass. Does not actually test visibility.
-radius_override <int>- Force a maximum vis radius, in units, regardless of whether an env_fog_controller specifies one.
-nosort- Don't sort (an optimization) portals.
-tmpin- Read portals from
\tmp\<mapname>. -tmpout- Write portals to
\tmp\<mapname>. -trace <start cluster> <end cluster>(in all games since )
)- Writes a linefile that traces the vis from one cluster to another for debugging map vis.
General
-low- Run as an idle-priority process.
-threads- Override the number of CPU threads used. Maximum is 16 threads (32 in

 , unlimited in
, unlimited in  )
) 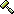 Workaround:With a patched vrad_dll you can use 32 threads.
Workaround:With a patched vrad_dll you can use 32 threads.  fixtoolthreads is a patch for VVIS (and VRAD) that supports unlimited threads and fixes a thread scaling issue.
fixtoolthreads is a patch for VVIS (and VRAD) that supports unlimited threads and fixes a thread scaling issue. Tip:If you know that the compile time will be very long and would rather do something else while waiting, it may be useful to specify a number of threads 1 or 2 lower than what your CPU has. This allows the computer to allocate some more power to other applications, making it less choppy while lighting is being compiled. Keep in mind that this may slightly extend your compile time.
Tip:If you know that the compile time will be very long and would rather do something else while waiting, it may be useful to specify a number of threads 1 or 2 lower than what your CPU has. This allows the computer to allocate some more power to other applications, making it less choppy while lighting is being compiled. Keep in mind that this may slightly extend your compile time.-verbose (-v)- Turn on verbose output
-novconfig- Don't bring up graphical UI on vproject errors.
-mpi- Use VMPI to distribute computations.
-mpi_pw <string>- Use a password to choose a specific set of VMPI workers.
-vproject <string>-game <string>- Override the VPROJECT environment variable.
Console Output
VVIS prints various information about the compile process to the console. Note that output from older versions of the tool can be different.
number portalclusters- The effective number of visleaves in the map (visleaves clustered together with func_viscluster count as one).
number numportals- The number of portals connecting the the above visleaves.
BasePortalVis: 0...1...2...3...4...5...6...7...8...9...10 (time taken in seconds)- Rough visibility calculations that are used to trivially weed out unseen areas from the final calculations.
PortalFlow: 0...1...2...3...4...5...6...7...8...9...10 (time taken in seconds)- Runs the actual visibility algorithm to determine which visleaves can see each other. Not run with
-fast. Optimized: number visible clusters (percentage)- Compression of the visibility data.
Total clusters visible: number- The total number of occurrences of visleaves being able to see each other in the calculated data.
Average clusters visible: number- The average number of leaves you can potentially see from each visleaf.
Building PAS...- Calculates the Potentially Audible Set.
Average clusters audible: number- The average number of leaves you can potentially hear into from each visleaf.
visdatasize: number compressed from number- Size of the visibility data in bytes. Max size is 16 MB in Source 2013.
See also
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||