VMPI: Difference between revisions
Kestrelguy (talk | contribs) m (updated language bar.) |
(Massive VMPI infodump/edit. Added performance tips section, updated gmod workaround section to include other games, fixed wrong port/setup info, etc.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{lang|VMPI}}{{source topicon}} | {{lang|VMPI}}{{source topicon}} | ||
{{obsolete|tool=1}} | {{obsolete|tool=1}} | ||
[[VMPI]] stands for "'''V'''alve '''M'''essage '''P'''assing '''I'''nterface". It was a previously unreleased tool by [[Valve]] used for distributed compiles of {{source| | [[VMPI]] stands for "'''V'''alve '''M'''essage '''P'''assing '''I'''nterface". It was a previously unreleased tool by [[Valve]] used for distributed compiles of {{source|4}} maps. The tool was quietly released around November of 2007 in an update that also included {{src07|4}} tools for mapping. Both the {{hl2ep1|4}} and the {{src07}} compile tools used VMPI for distributed map compiles, though the latter's tool text help was not updated to show any new commands. | ||
The most accepted reason for Valve not releasing VMPI until late 2007 was because it required a MySQL server for tracking network statistics across the master and worker machines. The VMPI released in 2009 did not require a MySQL server and therefore didn't have a license restriction for using external code and programs. | The most accepted reason for Valve not releasing VMPI until late 2007 was because it required a MySQL server for tracking network statistics across the master and worker machines. The VMPI released in 2009 did not require a MySQL server and therefore didn't have a license restriction for using external code and programs. | ||
{{bug| | |||
Both [[VVIS]] and [[VRAD]] have been improved over the years to better scale across modern high thread count CPU's. This, alongside the fact that the VRAD part of this tool is non-functional, means properly setting up a VMPI "compile farm" is considered to be more effort than it's worth by most. That being said, it has been proven to reduce compile times significantly if set up correctly. | |||
{{bug|the VRAD part of this tool has been broken since before SteamPipe (specifically 2009) and immediately crashes. This tool is only useful for distributed VVIS compiles for most games. Fixed in {{gmod}}.{{confirm}}}} | |||
{{Warning|VMPI is very neglected. It may be partially or entirely broken depending on the game you are working with, or require extra dependencies that are not public. VVIS is still functional with most {{src}} tools (such as {{csgo}} and {{tf2}}), but your mileage may vary!}} | |||
==VMPI Usage== | ==VMPI Usage== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 15: | ||
Before you start a VMPI compile, you need to have at least two machines (one master and one worker). The worker machine(s) must also have at least Windows 2000 installed (Windows 95-series OSs are not supported). | Before you start a VMPI compile, you need to have at least two machines (one master and one worker). The worker machine(s) must also have at least Windows 2000 installed (Windows 95-series OSs are not supported). | ||
* To start a master machine in {{hammer|4}}, all you need to do is add the "-mpi" flag to the compile parameters of both [[VVIS]] and [[VRAD]]. [[VBSP]] cannot be run in VMPI mode, | * To start a master machine in {{hammer|4}}, all you need to do is add the "-mpi" flag to the compile parameters of both [[VVIS]] and [[VRAD]]. [[VBSP]] cannot be run in VMPI mode, as the BSP information must be compiled on the master before being sent to the workers. You will want to add "-low" as well if you plan on using this machine during the compile process. | ||
* Starting a worker machine is somewhat different. First, you need to select the right version of compile tools for the job. {{src06|4}} compile tools are not VMPI compatible with {{src07|4}} tools and vice versa. After you figure that out, open a command console (cmd.exe) and navigate to the directory with the compile tools. You can generally use these shortcuts in the command console to get there quicker: | * Starting a worker machine is somewhat different. First, you need to select the right version of compile tools for the job. {{src06|4}} compile tools are not VMPI compatible with {{src07|4}} tools and vice versa. After you figure that out, open a command console (cmd.exe) and navigate to the directory with the compile tools. You can generally use these shortcuts in the command console to get there quicker: | ||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
'''cd %steamdir%\common\[source-engine game name]\bin''' | '''cd %steamdir%\common\[source-engine game name]\bin''' | ||
Once you' | Once you've found the bin folder on your worker machine, look for vrad.exe and vvis.exe. Open them with a batch script or windows shortcut with the following flags: | ||
'''vvis.exe -mpi_worker <master IP Address>:<port> -mpi_retry''' | |||
'''vrad.exe -mpi_worker <master IP Address>:<port> -mpi_retry''' | |||
{{Note|It is highly recommended that you create a simple watchdog script to re-launch VVIS/VRAD with these flags on crash, to avoid needing to constantly restart VVIS/VRAD on the worker if the map fails to compile, or for debugging the VMPI configuration in general.}} | |||
{{Tip|Default port is 23311. Specifying the port is only necessary for over-the-internet compiles, and can be omitted for LAN MPI}} | |||
{{Tip|Add the <code>-low</code> flag if you plan on using the worker machines for something else during the compile process.}} | |||
If you get an error about missing gameinfo.txt, add this additional flag to tell it where gameinfo.txt is: | If you get an error about missing gameinfo.txt, add this additional flag to tell it where gameinfo.txt is: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 54: | ||
{{def|code=1|-mpi}} Enable VMPI mode on the master machine. | {{def|code=1|-mpi}} Enable VMPI mode on the master machine. | ||
{{def|code=1|-mpi_Worker}} Used on the worker machine to connect to the master machine. Put the IP Address of the master machine after the command. (Ex: -mpi_worker 192.168.1.100) | {{def|code=1|-mpi_Worker}} Used on the worker machine to connect to the master machine. Put the IP Address of the master machine after the command. (Ex: -mpi_worker 192.168.1.100) | ||
{{def|code=1|-mpi_Port}} Used on the master | {{def|code=1|-mpi_Port}} '''Used only on the master machine''' to change the default port number to something else. (Ex: -mpi_Port 2946) The default port VMPI uses is 23311. Worker machines ports are defined using <code>-mpi_Worker <master IP address>:<port></code> instead. | ||
{{def|code=1|-mpi_Graphics}} Used on the master machine to show a graphical output of the work that's being done. If you have ever used the Windows 9x defragmentation utility, this will look similar to that. | {{def|code=1|-mpi_Graphics}} Used on the master machine to show a graphical output of the work that's being done. If you have ever used the Windows 9x defragmentation utility, this will look similar to that. | ||
[[Image:Vmpi animated.gif|350px|thumb|right|VMPI graphical output example, animated.]] | [[Image:Vmpi animated.gif|350px|thumb|right|VMPI graphical output example, animated.]] | ||
| Line 64: | Line 75: | ||
* '''-mpi_TrackEvents''' | * '''-mpi_TrackEvents''' | ||
Used on the master machine to enable a debug menu during compiles ("-mpi_Graphics" automatically enables it.) To access the menu, press "D" on the keyboard during a compile. | Requires administrator privileges. Used on the master machine to enable a debug menu during compiles ("-mpi_Graphics" automatically enables it.) To access the menu, press "D" on the keyboard during a compile. May be buggy | ||
* '''-mpi_ShowDistributeWorkStats''' | * '''-mpi_ShowDistributeWorkStats''' | ||
| Line 77: | Line 88: | ||
* '''-mpi_AutoLocalWorker''' | * '''-mpi_AutoLocalWorker''' | ||
Used on the master machine to spawn a local worker on the master machine. Only used for testing. | Used on the master machine to spawn a local worker on the master machine. Only used for testing. | ||
{{Bug|Doesn't seem to function with {{tf2}} tools? worker count still displays as 1 when used with a separate worker, use '''-mpi_Local''' instead.{{confirm}}}} | |||
* '''-mpi_Local''' | |||
Similar to -mpi_AutoLocalWorker, but the automatically-spawned worker's console window is hidden. | |||
* '''-mpi_FileTransmitRate''' | * '''-mpi_FileTransmitRate''' | ||
| Line 88: | Line 104: | ||
== Over the Internet == | == Over the Internet == | ||
If you intend to compile over the internet, you must make sure that the end where the master resides has proper port forwarding through its router (if any exist). The default is port 23311 on both TCP and UDP. If you intend to use a non-standard port, make sure that the port is also forwarded on both TCP and UDP. | If you intend to compile over the internet, you must make sure that the end where the master resides has proper port forwarding through its router (if any exist). The default is port 23311 on both TCP and UDP. If you intend to use a non-standard port, make sure that the port is also forwarded on both TCP and UDP. Workers do not need their ports forwarded. | ||
== | {{Note|Large maps compiled in MPI mode with a very slow internet connection to the workers can potentially outweigh the compile time improvements of a VMPI setup in the first place! Make sure the worker/master machines have enough bandwidth to quickly send BSP files with embedded VVIS/VRAD data to eachother.}} | ||
In order to get VMPI working on | |||
== Known problems and workarounds == | |||
In order to get VMPI working on {{gmod}} {{tf2}} or {{l4d}}{{confirm}} tools, you must create 2 blank text files in the '''BIN''' folder of the master where VVIS and VRAD are stored called: | |||
* '''dependency_info_vvis.txt''' | * '''dependency_info_vvis.txt''' | ||
| Line 97: | Line 115: | ||
* '''dependency_info_vrad.txt''' | * '''dependency_info_vrad.txt''' | ||
{{tf2}}{{csgo}} The compiled bsp will attempt to be loaded directly from the vvis launch parameters, causing your worker machine to crash trying to open an invalid map (such as -mpi_retry.bsp). This behavior likely exists in other games but has only been observed in the two mentioned. | |||
{{workaround|Manually add the name of your map to the launch parameters for the vvis/vrad worker. For example: <code>vvis.exe -mpi_worker 192.168.0.999 -mpi_retry map_name</code>. Do not include the .bsp extension}} | |||
{{gmod}} If you do not utilize the '''-mpi_AutoRestart''' flag for MPI VRAD, you must restart the workers when compiling HDR lighting. | |||
{{gmod}} The only way to get VMPI to work is by creating a bat file/shortcut to '''vvis.exe''' and '''vrad.exe''' with all the flags you need. Don't use third party tools like '''VBCT'''{{confirm}} | |||
==CS:GO workaround== | ==CS:GO workaround== | ||
[[Image:Vvis vmpi patch.png|350px|thumb|right|Figure 1: vvis_dll.dll patching]] | [[Image:Vvis vmpi patch.png|350px|thumb|right|Figure 1: vvis_dll.dll patching]] | ||
Adding ''- | Adding ''-mpi'' to the CS:GO vvis or vrad will display an error: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | ||
Initializing VMPI... | Initializing VMPI... | ||
VMPI running in SDK mode but incorrect SDK install detected (error 0). | VMPI running in SDK mode but incorrect SDK install detected (error 0). | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
You can circumvent this by patching the dll file to jump over the corresponding if statement. This trick will work for ''vvis_dll.dll'' but '''not''' ''vrad_dll.dll'', which probably inherited its brokenness from earlier versions of Source. You can download a pre-patched version [https://cm2.network/csgo/bin.zip here. (Mirror: CM2.Network)] | You can circumvent this by patching the dll file to jump over the corresponding if statement. This trick will work for ''vvis_dll.dll'' but '''not''' ''vrad_dll.dll'', which probably inherited its brokenness from earlier versions of Source. You can download a pre-patched version [https://cm2.network/csgo/bin.zip here. (Mirror: CM2.Network)] | ||
{{Warning|Outdated. Please take notice of the [[Increased_Thread_Limit_for_Compile_Tools#Disclaimer|disclaimer]] and back up your original ''vvis_dll.dll'' and ''vrad_dll.dll'' before you replace them.}} | |||
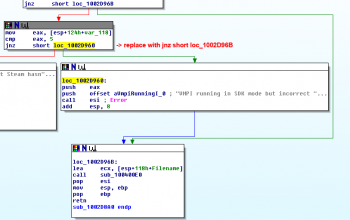
{{note|If you have an advanced knowledge of assembly, you can find the if statement via cross-referencing the string "VMPI running in SDK mode but incorrect SDK install detected (%n).". Then you can replace the jump to skip the error throwing subroutine. (Figure 1)}} | {{note|If you have an advanced knowledge of assembly, you can find the if statement via cross-referencing the string "VMPI running in SDK mode but incorrect SDK install detected (%n).". Then you can replace the jump to skip the error throwing subroutine. (Figure 1)}} | ||
| Line 123: | Line 143: | ||
* '''-mpi_Job_Watch''' | * '''-mpi_Job_Watch''' | ||
Automatically launches vmpi_job_watch.exe on the job. | Automatically launches vmpi_job_watch.exe on the job. | ||
* '''-mpi_DontSetThreadPriorities''' | * '''-mpi_DontSetThreadPriorities''' | ||
| Line 162: | Line 179: | ||
* '''-mpi_filebase''' | * '''-mpi_filebase''' | ||
??? | ??? | ||
==Performance tips== | |||
VMPI distributes the workload for VVIS and VRAD across the master and worker CPUs, causing your compile times to only be as fast as the slowest worker in the chain. Improperly configured MPI setups that do not consider this can cause compile times that are '''Slower''' than a standard, non-MPI compile. | |||
An example of an '''incorrect''' VMPI configuration would be a slow, spare worker computer connected to a fast master computer, in the hopes of simply allocating those extra threads to speed up the compile. This setup will be limited by the slower computer and actually '''Increase compile times''', rather than simply adding the extra processing power to the job and utilizing both CPU's at 100% capacity. | |||
Slow master/fast worker setups will also be bottlenecked, so the optimal VMPI setup is one where all workers, and the master, use the same brand/configuration of CPU (or at the very least, ones with identical performance). | |||
{{Todo|Unlikely, but see if <code>-mpi_NoMasterWorkerThreads</code> has any effect on extreme cases of slow master/fast worker performance. You should probably be doing the entire compile via remote desktop for situations like this though}} | |||
====Performance results (old)==== | |||
{{Todo|Update/add VVIS benchmarks for identical master/worker CPU's over LAN.}} | |||
[[Image:Vmpi vvis test.png|350px|thumb|right|Figure 2: Patched vvis_dll.dll running VMPI on 10 machines]] | [[Image:Vmpi vvis test.png|350px|thumb|right|Figure 2: Patched vvis_dll.dll running VMPI on 10 machines]] | ||
{{note|The tests were conducted with an unoptimised .vmf file to handle the worst case. Also the results show only VVIS.}} | {{note|The tests were conducted with an unoptimised .vmf file to handle the worst case. Also the results show only VVIS.}} | ||
| Line 178: | Line 206: | ||
==(Un)official tools== | ==(Un)official tools== | ||
[ | [[Batch Compile Tool]] An older compile tool similar to [[Compile Pal]], however it offers a GUI for configuring VMPI launch parameters and port information. Not recommended for use with {{gmod}}{{confirm}}. | ||
[https://archive.org/details/SourceExtendedNetCompiler SENC(Outdated)] Provides a GUI for VMPI compiles for Episode 1 and Episode 2 maps. Not recommended and may be entirely non-functional. | |||
SENC workers come with a fake (but not in an illegal sense!) Steam installation, allowing you to run workers on whatever machine you please. | |||
{{sdktools}} | {{sdktools}} | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 27 January 2023
VMPI stands for "Valve Message Passing Interface". It was a previously unreleased tool by Valve used for distributed compiles of ![]() Source maps. The tool was quietly released around November of 2007 in an update that also included
Source maps. The tool was quietly released around November of 2007 in an update that also included ![]() Source 2007 tools for mapping. Both the
Source 2007 tools for mapping. Both the ![]() Half-Life 2: Episode One and the
Half-Life 2: Episode One and the ![]() compile tools used VMPI for distributed map compiles, though the latter's tool text help was not updated to show any new commands.
compile tools used VMPI for distributed map compiles, though the latter's tool text help was not updated to show any new commands.
The most accepted reason for Valve not releasing VMPI until late 2007 was because it required a MySQL server for tracking network statistics across the master and worker machines. The VMPI released in 2009 did not require a MySQL server and therefore didn't have a license restriction for using external code and programs.
Both VVIS and VRAD have been improved over the years to better scale across modern high thread count CPU's. This, alongside the fact that the VRAD part of this tool is non-functional, means properly setting up a VMPI "compile farm" is considered to be more effort than it's worth by most. That being said, it has been proven to reduce compile times significantly if set up correctly.
VMPI Usage
VMPI requires that worker machines are manually started in polling mode before the master starts a compile. It also means that a local copy of Steam must be installed on the worker machines and at least one ![]() Source game installed.
Source game installed.
Before you start a VMPI compile, you need to have at least two machines (one master and one worker). The worker machine(s) must also have at least Windows 2000 installed (Windows 95-series OSs are not supported).
- To start a master machine in
 Hammer, all you need to do is add the "-mpi" flag to the compile parameters of both VVIS and VRAD. VBSP cannot be run in VMPI mode, as the BSP information must be compiled on the master before being sent to the workers. You will want to add "-low" as well if you plan on using this machine during the compile process.
Hammer, all you need to do is add the "-mpi" flag to the compile parameters of both VVIS and VRAD. VBSP cannot be run in VMPI mode, as the BSP information must be compiled on the master before being sent to the workers. You will want to add "-low" as well if you plan on using this machine during the compile process.
- Starting a worker machine is somewhat different. First, you need to select the right version of compile tools for the job.
 Source 2006 compile tools are not VMPI compatible with
Source 2006 compile tools are not VMPI compatible with  Source 2007 tools and vice versa. After you figure that out, open a command console (cmd.exe) and navigate to the directory with the compile tools. You can generally use these shortcuts in the command console to get there quicker:
Source 2007 tools and vice versa. After you figure that out, open a command console (cmd.exe) and navigate to the directory with the compile tools. You can generally use these shortcuts in the command console to get there quicker:
cd %steamdir%\common\Source SDK Base 2006\bin
cd %steamdir%\common\Source SDK Base 2007\bin
- SteamPipe:
cd %steamdir%\common\[source-engine game name]\bin
Once you've found the bin folder on your worker machine, look for vrad.exe and vvis.exe. Open them with a batch script or windows shortcut with the following flags:
vvis.exe -mpi_worker <master IP Address>:<port> -mpi_retry
vrad.exe -mpi_worker <master IP Address>:<port> -mpi_retry
-low flag if you plan on using the worker machines for something else during the compile process.
If you get an error about missing gameinfo.txt, add this additional flag to tell it where gameinfo.txt is:
-game "path_to_gameinfo.txt"
Example:
-game "%sourcesdk%\..\half-life 2\hl2"
Optional Commands
There are several additional options you can set on the compile tools which show things like stats and the total work done. Here is a complete list of the VMPI related commands on the compile tools:
- -mpi
- Enable VMPI mode on the master machine.
- -mpi_Worker
- Used on the worker machine to connect to the master machine. Put the IP Address of the master machine after the command. (Ex: -mpi_worker 192.168.1.100)
- -mpi_Port
- Used only on the master machine to change the default port number to something else. (Ex: -mpi_Port 2946) The default port VMPI uses is 23311. Worker machines ports are defined using
-mpi_Worker <master IP address>:<port>instead. - -mpi_Graphics
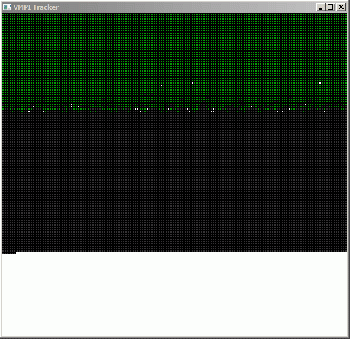
- Used on the master machine to show a graphical output of the work that's being done. If you have ever used the Windows 9x defragmentation utility, this will look similar to that.
- Grey Blocks - Work units not yet sent.
- Green Blocks - Completed work units.
- Light Green Blocks - Work units assigned to master.
- Blue Blocks - Work units assigned to worker machines.
- Red Blocks - Mentioned as "sent work", usually not seen.
Blue and light green blocks are more specifically single CPUs on a worker and master. If a worker or master has multiple CPUs or CPUs with multiple cores, it will be represented by additional dots. Dual cores will be two, quads will be 4, etc.
Here is an example of 18 processors working on compiling a single map (16 worker CPUs + 2 master.) What's great about the current VMPI is that if you have the correct ports forwarded on your router, you can have machines all over the world help you compile your map. A caveat in this is that both the master and worker machines need decent internet connections with lots of bandwidth, or the workers can time out while downloading resources from the master and slow the compile down.
- -mpi_Retry
Used on a worker machine to keep polling a specified master until the master starts a compile. If not used before a master machine starts a compile, the worker will time out and display an "MPI_Init failed" error.
- -mpi_AutoRestart
Used on a worker machine to auto-restart polling mode after a compile is finished. This command is buggy and doesn't always work, so don't rely on it. Must be used in conjunction with "-mpi_Retry" if you don't want to keep getting the "MPI_Init failed" message.
- -mpi_TrackEvents
Requires administrator privileges. Used on the master machine to enable a debug menu during compiles ("-mpi_Graphics" automatically enables it.) To access the menu, press "D" on the keyboard during a compile. May be buggy
- -mpi_ShowDistributeWorkStats
Shows the statistics of the workers used in the compile and how much work they have completed. Statistics are shown after the compile is completed.
- -mpi_TimingWait
Used on the master to delay the compile until a keystroke is pressed. Useful to let workers connect before the master starts the compile.
- -mpi_WorkerCount
Used on the master to set the maximum amount of workers allowed in the job.
- -mpi_AutoLocalWorker
Used on the master machine to spawn a local worker on the master machine. Only used for testing.
- -mpi_Local
Similar to -mpi_AutoLocalWorker, but the automatically-spawned worker's console window is hidden.
- -mpi_FileTransmitRate
Throttles the rate at which files can be downloaded from the master machine to any given worker machine.
- -mpi_Verbose
Level of debug output by VMPI. Either 0, 1 or 2.
- -mpi_NoMasterWorkerThreads
Don't process work units locally (on the master.) Useful if you only want the master to track compiled data instead of processing work units.
Over the Internet
If you intend to compile over the internet, you must make sure that the end where the master resides has proper port forwarding through its router (if any exist). The default is port 23311 on both TCP and UDP. If you intend to use a non-standard port, make sure that the port is also forwarded on both TCP and UDP. Workers do not need their ports forwarded.
Known problems and workarounds
In order to get VMPI working on ![]()
![]() or
or ![]() [confirm] tools, you must create 2 blank text files in the BIN folder of the master where VVIS and VRAD are stored called:
[confirm] tools, you must create 2 blank text files in the BIN folder of the master where VVIS and VRAD are stored called:
- dependency_info_vvis.txt
- dependency_info_vrad.txt
![]()
![]() The compiled bsp will attempt to be loaded directly from the vvis launch parameters, causing your worker machine to crash trying to open an invalid map (such as -mpi_retry.bsp). This behavior likely exists in other games but has only been observed in the two mentioned.
The compiled bsp will attempt to be loaded directly from the vvis launch parameters, causing your worker machine to crash trying to open an invalid map (such as -mpi_retry.bsp). This behavior likely exists in other games but has only been observed in the two mentioned.
vvis.exe -mpi_worker 192.168.0.999 -mpi_retry map_name. Do not include the .bsp extension![]() If you do not utilize the -mpi_AutoRestart flag for MPI VRAD, you must restart the workers when compiling HDR lighting.
If you do not utilize the -mpi_AutoRestart flag for MPI VRAD, you must restart the workers when compiling HDR lighting.
![]() The only way to get VMPI to work is by creating a bat file/shortcut to vvis.exe and vrad.exe with all the flags you need. Don't use third party tools like VBCT[confirm]
The only way to get VMPI to work is by creating a bat file/shortcut to vvis.exe and vrad.exe with all the flags you need. Don't use third party tools like VBCT[confirm]
CS:GO workaround
Adding -mpi to the CS:GO vvis or vrad will display an error:
Initializing VMPI...
VMPI running in SDK mode but incorrect SDK install detected (error 0).
You can circumvent this by patching the dll file to jump over the corresponding if statement. This trick will work for vvis_dll.dll but not vrad_dll.dll, which probably inherited its brokenness from earlier versions of Source. You can download a pre-patched version here. (Mirror: CM2.Network)
Additional CS:GO VMPI specific commands
These are additional optional (some hidden) arguments found in the CSGO vvis_dll.dll:
- -mpi_CalcShuffleCRC
Calculate a CRC for shuffled work unit arrays in the SDK work unit distributor.
- -mpi_Job_Watch
Automatically launches vmpi_job_watch.exe on the job.
- -mpi_DontSetThreadPriorities
Don't set worker thread priorities to idle.
- -mpi_GroupPackets
Delay and group some of the worker packets instead of sending immediately.
- -mpi_Stats
Enables the use of a database to store compile statistics.
- -mpi_Stats_TextOutput
Enables the workers storing all of their text output into the stats database.
- -mpi_NoScheduler
Warning - this should only be used for testing and with 1 worker!
- -mpi_NoTimeout
Don't timeout VMPI sockets. Used for testing.
- -mpi_SDKMode
Force VMPI to run in SDK mode.
- -mpi_UseDefaultDistributor
Use the default work unit distributor. Optimized for high numbers of workers, higher numbers of work units, and lower latency. Note that this will automatically be used in non-SDK distributions. --Walki: Tested & Broken unfortunatly
- -mpi_UseSDKDistributor
Use the SDK work unit distributor. Optimized for low numbers of workers and higher latency. Note that this will automatically be used in SDK distributions.
- -mpi_MasterName
???
- -mpi_file
???
- -mpi_filebase
???
Performance tips
VMPI distributes the workload for VVIS and VRAD across the master and worker CPUs, causing your compile times to only be as fast as the slowest worker in the chain. Improperly configured MPI setups that do not consider this can cause compile times that are Slower than a standard, non-MPI compile.
An example of an incorrect VMPI configuration would be a slow, spare worker computer connected to a fast master computer, in the hopes of simply allocating those extra threads to speed up the compile. This setup will be limited by the slower computer and actually Increase compile times, rather than simply adding the extra processing power to the job and utilizing both CPU's at 100% capacity.
Slow master/fast worker setups will also be bottlenecked, so the optimal VMPI setup is one where all workers, and the master, use the same brand/configuration of CPU (or at the very least, ones with identical performance).
-mpi_NoMasterWorkerThreads has any effect on extreme cases of slow master/fast worker performance. You should probably be doing the entire compile via remote desktop for situations like this thoughPerformance results (old)
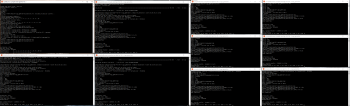
VMPI performance appears to be pretty bad compared to the amount of CPUs you have to invest. Take these tests with a pinch of salt as there could have been the following performance influences: wine (to run VVIS on Linux) and VPS (multiple vCores splitting the same physical core).
- 10 x 4 vCores (1.80GHz) (VMPI, ~100% Usage): 1 hour, 12 minutes, 3 seconds elapsed (Figure 2)
- 4 physical cores (3.4GHz) (8 threads, ~100% Usage) + 4x4 vCores (VMPI): 47 minutes, 1 second elapsed
As a comparison here is a pure local compile:
- 4 physical Cores (8 threads, ~100% Usage): 52 minutes, 53 seconds elapsed
The tests show that a combination of dedicated high frequency and numerous low frequency VPS CPUs are the optimal way to go if you want to use VMPI to it's best extend. During the end of the compile process some CPUs will work on the same world unit (WU) which makes it likely that a high frequency CPU will finish this task first thus not leaving all the other cpus idling like in a 32 threads compile.
(Un)official tools
Batch Compile Tool An older compile tool similar to Compile Pal, however it offers a GUI for configuring VMPI launch parameters and port information. Not recommended for use with ![]() [confirm].
[confirm].
SENC(Outdated) Provides a GUI for VMPI compiles for Episode 1 and Episode 2 maps. Not recommended and may be entirely non-functional.
SENC workers come with a fake (but not in an illegal sense!) Steam installation, allowing you to run workers on whatever machine you please.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||