FGD
You can help by updating the translation.
Also, please make sure the article complies with the alternate languages guide.
This notice is put here by LanguageBar template and if you want to remove it after updating the translation you can do so on this page.
FGD (Forge Game Data) é um formato de arquivo de texto simples usado para definir todas as entidades de um jogo para um editor de mapas, permitindo que os mapeadores possam selecionar a partir do editor e configure suas propriedades.
Embora Hammer fosse originalmente chamado de ![]() Worldcraft, ele foi desenvolvido sob o nome de The Forge (daí o nome Forge Game Data). Devido a questões de marca registrada, entretanto, o nome Forge não pôde ser usado na versão final do Hammer. Mesmo assim, a extensão do arquivo permaneceu.
Worldcraft, ele foi desenvolvido sob o nome de The Forge (daí o nome Forge Game Data). Devido a questões de marca registrada, entretanto, o nome Forge não pôde ser usado na versão final do Hammer. Mesmo assim, a extensão do arquivo permaneceu.
Para que os arquivos FGD personalizados funcionem no Hammer ou Jack, eles devem ser adicionados em Ferramentas > Opções.
@include "base.fgd" na parte superior do seu FGD e ele for carregado antes de base.fgd, você encontrará erros.Você não pode criar ou modificar entidades editando um FGD, você apenas fornece ao editor de mapas informações diferentes sobre o que ele espera encontrar no jogo. Às vezes, a edição revela recursos ou até entidades ocultas ou não utilizadas, mas elas sempre estiveram lá e poderiam ser usadas mesmo sem o FGD atualizado.
Prefer editor-agnostic language when not referring to a specific editor; unless something is specific to Hammer, refer to the program used to create maps as "the map editor". If it is specific to Hammer, specify the major version (3.x, 4.x, 5.x).
File Format
An FGD file consists of keywords that start with an @ character that might be followed by properties or even a body surrounded with square brackets [ ]. This may be the definition of an entity class or any other information that the map editor will use, depending on the keyword. In the following, all the different types of keywords are covered.
Comments can only be added as line comments, starting with //. Block comments or multiline comments are not supported.
//====== Copyright © 1996-2005, Valve Corporation, All rights reserved. ======= // // Purpose: Half-Life 2 game definition file (.fgd) // //=============================================================================
Entities
The syntactic components of an entity structure as defined in the FGD include:
- the class type of the entity (
@PointClass), - (optional) whitespace delimited class properties (
base(...) studio(...)), - an equals sign and the classname of the entity (
example_entity_name), - (optional) a colon followed by a description for it (
"...") and - a body surrounded by square brackets
[ ]containing the entity's keyvalues, flags and Inputs and Outputs.
Explanations of what each of these parameters do will be explained on this page, in order.
@PointClass base(Targetname, Angles, Origin) studio("path/model.mdl") = example_entity_name : "example entity description, visible in Hammers 'help' Box.
[
Property_name_1(string) : "Example String Name" : "Example" : "Keyvalue Description"
Property_name_2(integer) : "Example Interger Name" : 15 : "Keyvalue Description"
Property_name_3(float) : "Example Float Name" : "1.5" : "Keyvalue Description"
Property_name_4(boolean) : "Example Boolean Name" : 1 : "Keyvalue Description"
Property_name_5(choices) : "second number" : 0 : "Your choice of numbers!" =
[
0 : "Default"
1 : "Something"
2 : "Another Thing"
]
spawnflags(flags) =
[
1 : "A flag" : 0 // 0 means the flag isn't ticked by default
2 : "Another flag" : 1 // 1 means the flag is ticked by default
]
// Inputs
input DoSomething(void) : "Do something"
// Outputs
output OnSomethingHappened(void) : "Fires when something happens"
output OnSomethingElse(void) : "Fires when something else happens"
]
Class Types and Properties
The class type of an entity tells Hammer how this entity can be placed.
| Class Name | Supported Editors | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @BaseClass | A set of properties that can be inherited, reducing clutter. See @BaseClass. | |
| @PointClass | Point Entity: This entity exists at a certain non-arbitrary point. These entities are placed within Hammer by using the Hammer Entity Tool, ⇧ Shift+E. | |
| @NPCClass | This is a special form of point entity tailored for NPC (Non-Player Character) entities. It is useful in conjunction with the npcclass property type (see below).
| |
| @SolidClass | Brush Entity: This entity has a volume that is defined by the solid (also referred to as a brush) that it is attached to. A solid is tied to an entity by selecting it and pressing Ctrl+T. Other solids are world brushes. | |
| @KeyFrameClass | Used for move_rope and keyframe_rope. This causes the NextKeysprite property to be linked up when the entity is copied.
| |
| @MoveClass | Used for path_track and similar entities. This causes the targetsprite property to be linked up when the entity is copied.
| |
| @FilterClass | One of the special filter classes used to define what entities will be able to interact with each other in some way. This mainly causes the entity to be shown in properties with the filterclass type.
|
Things between the class type declaration and the "= <entity_name_here>" help to define properties of the entity, how it will act and be displayed in Hammer.
There are a number of different keywords that can used here. Multiple of these can be used, each separated by a space.
| Property | Supported Editors | Description |
|---|---|---|
| axis( property ) | Allows positioning two points joined by a line in the map. The property value is set to "x1 y1 z1, x2 y2 z2" by default. | |
| base( BaseClass1, BaseClass2, … ) | This lets you attach previously defined BaseClasses (see below) to an entity. You can specify multiple BaseClasses, each separated by a comma.
| |
| bbox( min,max ) | Sets the size of the entity's bounding box. | |
| color( red green blue ) | This setting will change the color of the wireframe box in the Hammer 2D views, as well as the 3D view if no model is present. If this isn't present, the color will default to magenta. The values specified here are the RGB values of a color, and each number has a range from 0 to 255. | |
| cylinder( color, start_key, start_name, start_radius, end_key, end_value, end_radius ) | Draw a cylinder between two entities. This is similar to line(), but with the addition of two radius properties that are looked up on the target entities. These define the size of the start and end of the cylinder.
| |
| flags(flagname(s)) | Allows for multiple different editor flags, separated by commas:
| |
| frustum( fov,near,far,color, pitch_scale ) | Creates a rectangular cone extending from the entity. FOV defines the spread angle (0-180). Near and far define at what distances will be highlighted. The color value defines what color the cone will be shown with. Pitch_scale allows inverting the pitch angle when rendering the cone. The first four values must be property names, the last is a literal. If not specified, values are taken from _fov, _nearplane, _farplane, and _light, respectively. pitch_scale is set to -1.
| |
| halfgridsnap | When moving this entity, it will snap to half the current grid size. This is somewhat special as it takes no arguments or parentheses. | |
| iconsprite( "path/sprite.ext" ) | If this is used, the specified sprite will be shown in the editor's 3D view instead of a flat-shaded colored box. This will work along-side the studio() or studioprop() commands. If no sprite name is set, it uses the model property.
Uses VMT in | |
| lightcone( inner_fov, outer_fov, color, pitch_scale ) | Renders the cone used on light_spot entities. inner_fov is the key for the innermost cone section, outer_fov is the outermost. pitch_scale allows inverting the pitch angle when rendering the cone. Values are taken from _inner_cone, _cone, and _light, respectively, if they aren't specified. This reads many other values corresponding to light_spot properties.
| |
| lightprop( "path/model.mdl" ) | Identical to studioprop(), except that the pitch of the model is inverted.
| |
| line( color, start_key, start_value, end_key, end_value ) | Draws a line between two entities. The value properties in this entity give the names to look for in the key property on other entities. key is usually set to targetname. The color sets the color of the line when the entity is not selected. The second entity defaults to this one if not set.
| |
| model({ "path": "path/file.ext", "frame": #, "skin": #, "scale": # }) | A more verbose alternative to studio() for displaying in-editor models, which supports rescaling the displayed model, displaying a specific skin, and display a specific frame of a Can also be used instead of "path" are optional.model() is only supported by Trenchbroom! If it is not necessary to use the extra features available, then studio() or iconsprite() should be used instead, to retain compatibility with other editors. | |
| obb( min,max ) | Identical to bbox but oriented to the entity's angles.
| |
| origin( property ) | Allows positioning a vector property in the map. | |
| sidelist( sides ) | Highlight brush faces listed in the given property (as a space-seperated ID list). If not specified, the property used is sides.
| |
| size( -x,-y,-z,+x,+y,+z ) | Defines the size of the default cube used when no model or sprite is specified. | |
| sphere( propertyname ) | If an entity has a radius of effect, like a sound for example, a sphere will be displayed in Hammer's 2D and 3D views. You need to specify the property that will control the sphere size. If no property is specified, it will look for a radius property.
| |
| studio( "path/model.mdl" ) | Identical to studioprop(), but the bounding box around the entity will ignore this model. This is useful for entities that don't render the model ingame.
In | |
| studioprop( "path/model.mdl" ) | If this is used, the entity will be displayed in the 3D view as the specified model. If no model is specified, the value of the entity's model property will be used, if available (Unless hardcoded). Multiple models can be defined.skin and rendercolor properties, similar to prop_dynamic. | |
| vecline( property ) | Allows positioning a vector property in the map. This also draws a line from the entity to the position. | |
| wirebox( min,max ) | Draws a bounding box for two properties. origin() helpers should be defined as well to allow moving the points.
|
The following helpers take no arguments and are special-cased for specific entity types:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| decal() | Renders decals on nearby surfaces. This uses the texture property to set the material to use. |
| overlay() | Renders overlays on a surface. (For info_overlay) |
| overlay_transition() | Renders overlays on the intersections between water and the shore. (For info_overlay_transition) |
| light() | Present on light; its use is unknown. Pendência: Figure out what this does.
|
| sprite() | Renders the sprite material specified in the model keyvalue (env_sprite and variants). For entity icons, use iconsprite.
|
| sweptplayerhull() | Draws 32x32x72-sized rectangular prisms at two points (point0 and point1), then links corners to show the space needed for one rectangle to move to the other's position. This also adds origin() helpers for those properties.
|
| instance() | Renders the instance in the map. It also generates additional properties dynamically corresponding to the instance parameters. |
| quadbounds() | Used for func_breakable_surf. Automatically sets the 4 corners of the textured face on save. Pendência: Does this also control the "error" keyvalue?
|
| worldtext() (apenas em |
Displays the contents of the message keyvalue in the 3D viewport.
|
Entity Description
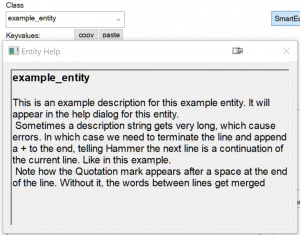
The entity description is a very important thing, as it the one single piece of help you can see in Hammer without consulting any website or developer, by pressing the "Help" button.
Each line of a description may not exceed 125 letters, in which case you must terminate the line and append a + at the end to start a new line in the FGD.
You may write \n To insert a line break, where hammer will start writing on a new line. You may also enter \n \n to skip one line entirely.
" " are not allowed inside the description, as this will terminate the string. Use Apostrophes ' ' instead.@PointClass = example_entity :
"This is an example description for this example entity. It will appear in the help dialog for this entity.\n " +
"Sometimes a description string gets very long, which cause errors. In which case we need to terminate the line and " +
"append a + to the end, telling Hammer the next line is a continuation of the current line. Like in this example.\n " +
"Note how the Quotation mark appears after a space at the end of the line. Without it, the words between lines get merged"
[
// (entity properties go here)
]
Entity Properties
Everything between the main set of square brackets [ ] is used to define the entity's properties, including their keyvalues, inputs and outputs.
Keyvalues
Individual keyvalues consist of
- a name of at most 31 characters,
- a value type declaration in round brackets,
- (optional) a colon followed by a string as the display name,
- (optional) a colon followed by either a default value or no value and
- (optional) a colon followed by a string as the description.
health(integer) health(integer) : "Strength" health(integer) : "Strength" : 1 health(integer) : "Strength" : 1 : "Number of points of damage to take before breaking. 0 means don't break." health(integer) : "Strength" : : "Number of points of damage to take before breaking. 0 means don't break."
The most common value types are:
| Property Type | Description |
|---|---|
| string | A character sequence. The default value must have quotation marks " " around it. |
| integer | A whole number. The default value may not be quoted. |
| float | A decimal number. The default value must be quoted unless it is a whole number with no decimal point. |
| boolean | A value that is either true (= 0) or false (not 0). This type needs a default value and it must be either 0 or 1. This creates a dropdown menu for the values Yes/No. For older versions of Hammer, use choices instead.
|
| flags | An integer value that is (supposed to be) read bitwise, making it ideal for multiple boolean values. See below. |
| choices | A value that must be one of a pre-defined set of values. This keyvalue type lets you setup a dropdown menu with a number of distinct choices.
Property_name_5(choices) : "Display name" : 1 =
[
// <value> : "Display Value"
0 : "something"
1 : "something else (default)"
2 : "something completely different"
]
You can also use strings (or floats) as values, instead of integers, like this: Property_name_5(choices) : "Model used" : "models/something02.mdl" =
[
"models/something01.mdl" : "something"
"models/something02.mdl" : "something else (default)"
"models/something03.mdl" : "something completely different"
]
|
Flags and Choices do not function as input/output types.
Property_name_1(string) : "Example String Name" : "Example" : "Keyvalue Description" Property_name_2(integer) : "Example Interger Name" : 15 : "Keyvalue Description" Property_name_3(float) : "Example Float Name" : "1.5" : "Keyvalue Description" Property_name_4(boolean) : "Example Boolean Name" : 1 : "Keyvalue Description"
There is also a number of special purpose property types that modify the entity properties dialog UI, for example to allow for easy browsing for files or easier manipulation of complex properties like colors or angles.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| angle | Adds an angle widget for this property to the entity dialog UI. |
| angle_negative_pitch | Identical to angle, except the pitch is inverted.
|
| axis | Adds a relative 2-point axis helper. |
| color255 | Adds a button that brings up the color choosing UI, which takes the color you select and translated it into the three-number RGB value. Allows extra parameters (e.g., brightness). |
| color1 | Adds a color button, but uses a float [0,1] instead of an integer (0,255). Allows extra parameters (e.g., brightness). |
| decal | Identical to material, except it will automatically replace your search filter with decals/ when opening the material browser.overlays/ or in another folder entirely. |
| filterclass | Marks property as being the name of the filter to use. |
| instance_file | Adds a button that brings up the file browser, letting you browse for instance files. |
| instance_parm | Used in func_instance_parms to define fixup variables. |
| instance_variable | Used in func_instance to set fixup variables. |
| material | Adds a button that brings up the material browser. |
| node_dest | adds an eyedropper to select a node in the 3d view |
| node_id | On nodes, this is used for the Node ID keyvalue to automatically increment it with each consecutive node placed. Does not appear to function when used on other entities. |
| npcclass | Adds a drop-down selection list populated by entities of the NPCClass type. |
| origin | origin |
| particlesystem | Adds a button that brings up the particle browser, letting you browse for particle systems. |
| pointentityclass | Adds a drop-down selection list populated by entities of the PointClass type.
|
| scene | Adds a button that brings up the sound browser, letting you browse for scene files. |
| script | Adds a button that brings up the file browser, letting you browse for VScripts. |
| scriptlist | Adds a button that brings up a list of VScripts with buttons to add/remove scripts and open each file. |
| sidelist | Adds a side selection eyedropper that allows you to choose sides (multiple with Ctrl). |
| sound | Adds a button that brings up the sound browser, letting you browse for soundscripts or raw sounds. |
| sprite | Identical to material, except it will automatically replace your search filter with sprites/ when opening the material browser, and it will add .vmt to the end of the material name.
|
| studio | Adds a button that brings up the model browser. |
| target_destination | Marks property as another entity's targetname.
|
| target_name_or_class | Marks property as another entity's targetname or classname.
|
| target_source | Marks property as being the name that other entities may target. |
| vecline | Adds an absolute 1-point axis helper, similar to the origin marker. |
| vector | 3D vector property. A string consisting of three space delimited numbers. |
Inputs and Outputs
Individual inputs and outputs consist of
- the keyword input or output,
- a name,
- a value type declaration in round brackets and
- (optional) a colon followed by a string as the description.
input Enable(void) input Enable(void) : "Enable this entity." output OnTakeDamage(void) output OnTakeDamage(void) : "Fired each time this breakable takes any damage."
The possible types include void, integer, float, string, bool where void means no value.
Flags
spawnflags(flags) = [ 1 : "Flag 01" : 0 2 : "Flag 02" : 0 4 : "Flag 03" : 0 8 : "Flag 04" : 0 16 : "Flag 05" : 0 32 : "Flag 06" : 0 64 : "Flag 07" : 0 128 : "Flag 08" : 0 256 : "Flag 09" : 0 512 : "Flag 10" : 0 1024 : "Flag 11" : 0 2048 : "Flag 12" : 0 4096 : "Flag 13" : 0 8192 : "Flag 14" : 0 16384 : "Flag 15" : 0 32768 : "Flag 16" : 0 65536 : "Flag 17" : 0 131072 : "Flag 18" : 0 262144 : "Flag 19" : 0 524288 : "Flag 20" : 0 1048576 : "Flag 21" : 0 2097152 : "Flag 22" : 0 4194304 : "Flag 23" : 0 8388608 : "Flag 24" : 0 16777216 : "Flag 25" : 0 33554432 : "Flag 26" : 0 67108864 : "Flag 27" : 0 134217728 : "Flag 28" : 0 268435456 : "Flag 29" : 0 536870912 : "Flag 30" : 0 1073741824 : "Flag 31" : 0 2147483648 : "Flag 32" : 0 ]
The flags tab of an entity is configured through its keyvalue named "spawnflags" using the value type "flags". This keyvalue type has a different syntax as seen in the following example:
- After spawnflags(flags) follows an equals sign and a body surrounded by square brackets [ ] containing a number of flags.
- Each flag consists of an integer as flag value, a colon, a display string and optionally another colon followed by a default value of 0 or 1.
The flag value should be a power of 2 (20=1, 21=2, 22=4, etc.).
Their default values are either 0 (off) or 1 (on), indicating that the flag's checkbox is either not ticked or ticked. If no default is specified, it is considered off.
spawnflags(flags) =
[
// <flag value 2^i> : "Checkbox Display Text" : <is ticked by default?>
1 : "something clever" : 1
2 : "something else" : 0
4 : "you said what now?" : 0
8 : "nothing" : 1
]
Due to an integer size of 4 bytes, there can be at most 32 disjoint flags. On the right is a template for all possible flag values, namely 20, ..., 231.
Other File Sections
@mapsize
This value defines the maximum usable area in Hammer. This visually changes the area in Hammer, but unless the game has been coded to allow this size, using anything beyond default values causes vbsp to crash.
@mapsize(-16384, 16384)
@include
If the game you are writing your FGD for has a lot in common with another game (![]() Half-Life 2 and
Half-Life 2 and ![]() Half-Life 2: Deathmatch, for example), you can
Half-Life 2: Deathmatch, for example), you can @include a file that has all of the common structures defined in it. This allows your FGD to read all the data of that FGD.
@Include can be nested. Meaning a game can include another game's FGD, which already includes the base.fgd. For example ![]() Half-Life 2: Deathmatch has a FGD which @include's
Half-Life 2: Deathmatch has a FGD which @include's halflife2.fgd, which in turn @include's the base.fgd.
The game or mod you are creating must ship with all FGD's that your own mod is including.
@include "base.fgd"
If you only need a few base classes and entities, it would be recommended to only copy those few into your own FGD.
@BaseClass
A BaseClass is used to setup structures that are used by several different entities via the base(BaseClassName) to the main definition line of the structure.
The BaseClass structure is defined just like a normal entity in all respects. The only difference is that it doesn't appear in the entity lists in Hammer.
@BaseClass = Angles [ angles(angle) : "Pitch Yaw Roll (Y Z X)" : "0 0 0" : "This entity's orientation in the world. Pitch is rotation around the Y axis, " + "yaw is the rotation around the Z axis, roll is the rotation around the X axis." ] @BaseClass = Origin [ origin(origin) : "Origin (X Y Z)" : : "The position of this entity's center in the world. Rotating entities typically rotate around their origin." ]
@MaterialExclusion
These lists define paths that Hammer's Material Browser will not use when presenting you with a palette of textures to choose from. It should have no effect on what files are actually available to a custom map.
models/ will always be excluded, regardless of what is set here.@MaterialExclusion
[
// Names of the sub-directories we don't want to load materials from
"debug"
"engine"
"hud"
"vgui"
]
@AutoVisGroup
This permits customizing the automatic Visgroups tab of the Filter Control toolbar. The first title is the name of the "parent," and the next is the "children." Finally comes a list of entity classes that will be placed in the visgroup.
If the parent already exists, the new entry will be merged with the previous ones (including the default list of groups). This permits creating trees with multiple levels of grouping. If a visgroup becomes entirely empty, it will not appear in the list.
You may add entities to existing groups if the "Parent" of the autovisgroup is the name of an existing group, like "World Details". For example, you could add func_brush to the list "World Details".
@AutoVisGroup = "Brushes"
[
"Triggers"
[
"trigger_once"
"trigger_multiple"
]
"Tool Brushes"
[
"func_areaportal"
"func_viscluster"
]
]
@AutoVisGroup = "Tool Brushes"
[
"Vis Clusters"
[
"func_viscluster"
]
]
Source 2 Additions
The following things have been found in ![]() Source 2 FGD files. These will not work in Source 1.
Source 2 FGD files. These will not work in Source 1.
Classes
- Examples of these Classes
// Add an override of player start in order to add it to the ui.
@OverrideClass
metadata
{
entity_tool_name = "Player Start"
entity_tool_group = "Player"
entity_tool_tip = "Entity which specifies where the player will start."
}
= info_player_start :
[
]
@OverrideClass = npc_cscanner
[
//Adds one single input to the npc_cscanner entity, which already existed in HL2 and is in halflife2.fgd
//Doing this is easier than completely redefining the entire entity.
input SpawnAsAltScanner(void): "Spawns the Russell skin/bodygroup scanner"
]
@CableClass = cable_static [ ] @CableClass base( Targetname, Parentname, Global, RenderFields, Glow, EnableDisable) sphere(fademindist) sphere(fademaxdist) = cable_dynamic [ secondary_material(material) : "Secondary Material" : "" : "Optional secondary material, can be selected using Skin(1)" lightingorigin(target_destination) : "Lighting Origin" : "" : "Select an entity to specify a location to sample lighting from, instead of using this entity's origin." disableshadows(boolean) [ group="Misc" ] : "Disable Shadows" : 0 : "Used to disable dynamic shadows on this entity." // Inputs input TurnOn(void) : "Make the prop visible." input TurnOff(void) : "Make the prop invisible." input Skin(integer) : "Changes the model skin to the specified number." input EnableCollision(void) : "Enable collision on the prop." input DisableCollision(void) : "Disable collision on the prop." input SetNavIgnore(boolean) : "Enable and disable NAVIgnore on the prop." input DisableShadow(void) : "Turn shadow off." input EnableShadow(void) : "Turn shadow on." input AlternativeSorting(bool) : "Used to attempt to fix sorting problems when rendering. True activates, false deactivates" input SetRenderAttribute(string) : "Set the value of a render attribute used in material dynamic expressions. Examples: $myfloat=0.25 $myfloat4=1.0,0.0,1.0,1.0" ]
@PathClass base(Targetname) tags( Particles ) particle_rope()
metadata
{
default_interpolation = "linear"
}
= path_particle_rope
[
effect_name(particlesystem) [report] : "Particle System Name" : "particles/entity/path_particle_cable_default.vpcf"
start_active(boolean) : "Start Active" : 1 : "Will the particle system be visible on spawn"
max_simulation_time(float) : "Max Time To Simulate" : 0 : "Max number of seconds to run the particle simulation for. A value of 0 means run the simulation indefinitely."
particle_spacing(float) : "Spacing" : 32 : "Units between the individual partcles in the rope simulation."
slack(float) : "Slack" : "0.5" : "Controls the amount the rope will drop between path nodes. Generally between 0.0 and 1.0, the value is a multiplier on the distance that particles on path can seperate relative to their initial distance."
radius(float) : "Radius" : "4.0" : "Radius of the rope."
static_collision( bool ) : "Create Static Collision" : "0" : "Create a static physics representation of the path. Note the collision is generated based on the path, movement applied by the particle system will not be included."
surface_properties(surface_properties) : "Surface Properties" : "" : "Surface properties to apply to the static collision if generated"
color_tint(color255) : "Color Tint" : "255 255 255"
// Inputs
input Start(void) : "Tell the particle system to start emitting."
input Stop(void) : "Tell the particle system to stop emitting."
input StopPlayEndCap(void) : "Tell the particle system to stop emitting and play its End Cap Effect."
input DestroyImmediately(void) : "Destroy the particle system and remove all particles immediately."
input SetRadius( float ) : "Set the radius parameter provided the particle system"
input SetSlack( float ) : "Set the slack parameter which may be used by the particle system to determine how much the rope droops."
input DisablePin( string ) : "Disable the contraint which pins a particle to the specified path node."
]
Other commands
| Class Name | Description |
|---|---|
| @Exclude | This can exclude individual entities that are in @include'd FGD's. One entity per line |
| @EntityGroup | Pendência: Explain what this does. |
| @struct | Pendência: Explain what this does. |
| @ModelGameData | Pendência: Explain what this does. Seems to work simillar to $keyvalues. |
| @ModelBreakCommand | Pendência: Explain what this does. Seems to work simillar to $collisiontext |
| @ModelAnimEvent | Pendência: Explain what this does. Seems to work simillar to Animation_Events in Sequences. |
| {{{1}}}} | Pendência: Explain what this does. |
| Deprecated() | Marks a property as depracated and no longer in use. |
- Examples of these commands
Below are expandable examples of the above listed commands.
We currently do not have any more good information on what these commands do, but at least we have examples of how to use them.
// Excluded entities. These are entities that are included from lower level fgd files that aren't // functional or useful in this mod. Excluding them removes them from the list of entities aviable // in Hammer or any other tool that loads the fgd. If support is added for any of the entities the // exclude can simply be removed. // These entities have been excluded because are deprecated light entities which are // explictly not supported, don't add these back unless you are working on lighting. @exclude color_correction_volume @exclude env_fog_controller @exclude env_time_of_day @exclude env_lightglow @exclude env_particlelight @exclude env_sun @exclude fog_volume @exclude info_lighting @exclude light_dynamic @exclude light_irradvolume @exclude point_spotlight @exclude postprocess_controller @exclude shadow_control
// Entity groups. This list specifies which entity groups will show up in the entity tool and in what
// order. If an entity specifies a group that is not in this list it will not be displayed in the tool.
// This allows the mod specific fgd to control the ui.
@EntityGroup "Player" { start_expanded = true }
@EntityGroup "Lighting" { start_expanded = true }
@EntityGroup "Fog & Sky" { start_expanded = true }
@EntityGroup "NPCs" { start_expanded = true }
@EntityGroup "Items"
@EntityGroup "Ammo"
@EntityGroup "Logic"
@ModelGameData = prop_data [ base(propdataname) : "Base Prop" : : "Base keys (entry from propdata.txt)" allowstatic(boolean) : "Allow As Static Prop" : 0 bakelighting(boolean) : "Bake Lighting As Static Prop" : 1 damage_table(choices) : "Damage Table" : "" : "" = [ "" : "Inherit Default" "player" : "Player" "player_vehicle" : "Player Vehicle" "npc" : "NPC" "glass" : "Glass" "props" : "Props" "prevent_impact_damage" : "Prevent All Impact Damage" ] dmg.bullets(float) : "Damage Bullets" : -1 dmg.club(float) : "Damage Club" : -1 dmg.explosive(float) : "Damage Explosive" : -1 dmg.fire(float) : "Damage Fire" : -1 health(float) : "Health" : -1 spawn_motion_disabled(boolean) : "Spawn as Motion-Disabled" : 0 ]
@ModelBreakCommand base(base_break_force) = break_uniform_burst : "Applies a radial burst to breakpieces outwards from the influence point (default is the origin of the model)" [ burst_scale(float) [ min="0", max="500" ] : "Burst Scale" : 0 : "Velocity added to each piece (radially away from the influence point)" burst_randomize(float) [ min="0", max="500" ] : "Burst Randomize" : 0 : "Magnitude of random vector that will be added to the burst velocity" ] @ModelBreakCommand base(base_break_force) = break_flip_pieces : "Applies an angular 'flip' to breakpieces (like objects tipping over from an explosion or flower petals opening) causing them to tip outwards from the influence point (default is the origin of the model)" [ burst_scale(float) [ min="-500", max="500" ] : "Flip Scale" : 0 : "Angular velocity added to each piece (Positive value will cause pieces to flip 'head-first' away from the influence point, negative is 'feet-first')" burst_randomize(float) [ min="0", max="500" ] : "Flip Randomize" : 0 : "Largest possible value that will be randomly added/removed to Flip Scale for each piece" ] @ModelBreakCommand base(base_break_force) = break_twist_pieces : "Applies an angular 'twist' to breakpieces, causing them to roll around the radial axis outward from the influence point (default is the origin of the model)" [ burst_scale(float) [ min="-500", max="500" ] : "Twist Scale" : 0 : "Angular velocity added to each piece" burst_randomize(float) [ min="0", max="500" ] : "Twist Randomize" : 0 : "Largest possible value that will be randomly added/removed to Twist Scale for each piece" ]
@ModelAnimEvent = AE_CL_PLAYSOUND_ATTACHMENT [ name(sound) [report] : "Sound" attachment(model_attachment) : "Attachment" stop_on_seq_change(bool) : "Auto-stop on sequence change or death" : "0" use_layer_sequence(bool) : "Use Layer Sequence" : "0" tags(string) : "Tags" ] @ModelAnimEvent = AE_COMPANION_PRODUCE_FLARE [ attachment(model_attachment) : "Attachment" ] @ModelAnimEvent = AE_STRIDER_SHOOTMINIGUN [ target(string) : "Target" ]
@PointClass base(BasePropPhysics, Targetname, Parentname ) model( "models/props_combine/health_charger/health_vial.vmdl" )
metadata
{
entity_tool_name = "Health Station Vial"
entity_tool_tip = "Vial used to power a health station"
entity_tool_group = "Items"
}
= item_hlvr_health_station_vial : "Health Vial"
[
vial_level(float) : "Health Vial Level (0-1)" : "1" : "Amount of health the vial starts with."
]
@ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_STRIDER_FOOTSTEP_LEFT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_STRIDER_FOOTSTEP_RIGHT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_STRIDER_FOOTSTEP_BACK [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_MARINE_FOOTSTEP [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_FOOTSTEP_LEFT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_FOOTSTEP_RIGHT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_SV_FOOTSTEP_LEFT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_SV_FOOTSTEP_RIGHT [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_ANTLION_FOOTSTEP_HEAVY [ ] @ModelAnimEvent deprecated() = AE_ANTLION_FOOTSTEP_SOFT [ ]
Files
The FGD files of a game can be found under <steam directory>/steamapps/common/<full game name>/bin/*.fgd, for example .../common/Half-Life 2/bin/halflife2.fgd.
See also
External links
- SE FGD's Updated FGD's for some Valve games, made by Pinsplash.
- Forge Game Data Language
.fgdsyntax highlighting available in textmate format (SublimeText Compatible)