SteamPipe: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Language subpage|title=SteamPipe}} {{todo|Most of the language subpages still use SteamPipe:….}} '''SteamPipe''' is Steam's new content distribution syst...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{LanguageBar|title = SteamPipe}} | ||
{{ | {{For|the Source 2013 engine branch, also referred as "SteamPipe branch"|[[Source 2013]]}} | ||
{{stub}} | |||
It changes the way programs (including [[dedicated server]]s) are downloaded, updated and stored. | '''SteamPipe''' is [[Steam]]'s content distribution system introduced in 2013. It changes the way programs (including [[dedicated server]]s and the [[Source]] engine) are downloaded, updated and stored. | ||
== Benefits == | == Benefits == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== Server administrators === | === Server administrators === | ||
Instead of a proprietary delivery protocol, SteamPipe uses HTTP, which allows datacenters hosting multiple servers to set up a caching HTTP proxy, necessitating only a single download of an update from Valve's servers. | Instead of a proprietary delivery protocol, SteamPipe uses HTTP, which allows datacenters hosting multiple servers to set up a caching HTTP proxy, necessitating only a single download of an update from Valve's servers. | ||
=== Game developers === | === Game developers === | ||
Game developers using SteamPipe can [http://garry.tv/2012/08/16/approved-updates/ issue updates themselves]; the previous system required manual intervention by Valve when an update was to be published. | Game developers using SteamPipe can [http://garry.tv/2012/08/16/approved-updates/ issue updates themselves]; the previous system required manual intervention by Valve when an update was to be published. | ||
=== LAN Caching === | === LAN Caching === | ||
As SteamPipe now uses HTTP it allows not only datacenters hosting multiple servers to setup a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caching_proxy#Caching_proxy_servers caching] but is also very useful for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network LAN's]. Setting up a caching proxy can significantly reduce the amount of bandwidth required for multiple clients or servers to preform updates. | As SteamPipe now uses HTTP it allows not only datacenters hosting multiple servers to setup a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caching_proxy#Caching_proxy_servers caching] but is also very useful for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network LAN's]. Setting up a caching proxy can significantly reduce the amount of bandwidth required for multiple clients or servers to preform updates. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 30: | ||
=== Players === | === Players === | ||
* Many {{hl2| | * Many Source SDK mods that use {{hl2|3.1}} (and/or its Episodes) content that did not make the jump to the update are broken, this also includes some (but not all) {{hl1|3.1}} mods.<br>Fortunately, there are known fixes for many Half-Life 2 mods. [https://web.archive.org/web/20230604114941/https://steamcommunity.com/app/420/discussions/0/864971765497379056/ Those fixes can be found here.]. | ||
* | * With {{src13|1}} and [[SteamPipe]], {{hl2|3.1}} base content are no longer shared across all Source Engine games, as a result, most {{src13|4.1}} games (including third-party games) now contain duplicate copies of the {{hl2|name}} base files {{hl2|in|addtext-front=''except'' |addtext={{hl2ep1}} {{hl2ep2}} {{hl2lc}} {{hls}}}}, wasting storage drive space. | ||
:{{warning|While the it is possible to point multiple games to the same VPK, not all VPKs with the same name are the same on all games! For example, the {{src13mp}} "hl2" VPKs are different from the VPKs actually used by {{hl2}}, | :{{warning|While the it is possible to point multiple games to the same VPK, not all VPKs with the same name are the same on all games! For example, the {{src13sp}} and {{src13mp}} "hl2" VPKs are different from the VPKs actually used by {{hl2}} (which contains additional content and incompatible [[shaders]] from 20th Anniversary Update), the {{tf2}} (including {{tf2branch|1}}) "hl2" VPKs are different from the other {{src13mp}} "hl2" VPKs.</br>'''As of 2025:''' Both {{hl2|1}} and {{portal|1}} runs on updated version of {{src13sp|1}} (20th Anniversary Update), and the "hl2" files in both games are nearly identical enough that the game function correctly, while {{src13sp|1}} still runs on older version of {{src13sp|1}} branch from 2014 and ships with older version of "hl2" folder containing VPKs incompatible with both games.<!-- | ||
-->{{workaround|Two options are such:<ul><li>Use relative links to the [[VPK]]s (or folders) in [[gameinfo.txt]], so they look something like this:<br><pre>game "../Half-Life 2/hl2/hl2_textures.vpk"</pre><li>Use Symbolic links or Hardlinking [[VPK]]s (or folders) using programs such as [https://schinagl.priv.at/nt/hardlinkshellext/linkshellextension.html Link Shell Extension] (easier), or via Windows's {{code|mklink}} command; [https://www.howtogeek.com/16226/complete-guide-to-symbolic-links-symlinks-on-windows-or-linux/ more info can be found here].</ul> | -->{{workaround|Two options are such:<ul><li>Use relative links to the [[VPK]]s (or folders) in [[gameinfo.txt]], so they look something like this:<br><pre>game "../Half-Life 2/hl2/hl2_textures.vpk"</pre><li>Use Symbolic links or Hardlinking [[VPK]]s (or folders) using programs such as [https://schinagl.priv.at/nt/hardlinkshellext/linkshellextension.html Link Shell Extension] (easier), or via Windows's {{code|mklink}} command; [https://www.howtogeek.com/16226/complete-guide-to-symbolic-links-symlinks-on-windows-or-linux/ more info can be found here].</ul> | ||
}} }} | }} }} | ||
*After the SteamPipe update, {{hls|4}} was not properly updated which resulted the game having more bugs and glitches, with graphical issues. This issue has never been fixed and Valve later instead de-listed the game from search (during {{hl|1}} 25th Anniversary Update) in favor of promoting the [[Half-Life|original version]] instead, 10 years after the SteamPipe update was released. | |||
*{{srcsdk07|1}} fails to mount {{hl2ep2|1}} assets properly, due to Valve mistakenly ships EP2 depot VPK files to {{srcsdk06|1}}. See [[Fixing VPK mounting for older Source SDK Bases]] for more information. | |||
=== Developers === | === Developers === | ||
The Source SDK Launcher does not have support for {{src13|4}} games. Tools for games that used to be in the Source SDK Launcher must now be launched by going to "C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\[game name]\bin" (see example path below) then launching the .bat files (Example: Hammer.bat to launch {{hammer|1|nt=1}}).<br><br> | |||
The Source SDK Launcher | |||
Example path to SDK: {{path|C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\Half Life 2\bin}} | Example path to SDK: {{path|C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\Half Life 2\bin}} | ||
== Changes == | == Changes == | ||
* Downloads are performed using HTTP instead of a proprietary protocol. | * Downloads are performed using HTTP instead of a proprietary protocol. | ||
* Data files are no longer placed into [[GCF]]s but directly into the file system. | * Data files are no longer placed into [[GCF]]s but directly into the file system. Games using {{src|1}} engine before {{l4dbranch|1}} no longer shares {{hl2|1}} base content between games. | ||
** To counteract the performance issues with accessing many tiny files (the reason why GCFs were used in the first place), [[Source]] games distributed via SteamPipe now store their assets in [[VPK]] archives. | ** To counteract the performance issues with accessing many tiny files (the reason why GCFs were used in the first place), all [[Source]] games (prior to {{l4d|1}}) distributed via SteamPipe now store their assets in [[VPK]] archives. | ||
* Data generated before/during gameplay is no longer stored in user-specific subdirectories of ''SteamApps''; instead, the ''common'' subfolder is used. | * Data generated before/during gameplay is no longer stored in user-specific subdirectories of ''SteamApps''; instead, the ''common'' subfolder is used. | ||
* Dedicated servers are using [[SteamCMD]] (a stripped-down version of the full Steam client). | * Dedicated servers are using [[SteamCMD]] (a stripped-down version of the full Steam client). | ||
== See | == See also == | ||
* [[ | * [[GoldSource SteamPipe Directories]] for the list of directories used by GoldSource engine games | ||
* [[IFileSystemV009]] for the C++ interface used to access files through SteamPipe in GoldSource | * [[IFileSystemV009]] for the C++ interface used to access files through SteamPipe in GoldSource | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20210419201507/https://support.steampowered.com/kb_article.php?ref=7388-QPFN-2491 Steam Support page] | |||
[[Category:CDN]] | |||
[[Category:Steam]] | |||
[[Category:Source]]<!-- Since this update affects Source games aswell. --> | |||
[[Category:Dedicated Server]]<!--Why?--> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:11, 2 October 2025
SteamPipe is Steam's content distribution system introduced in 2013. It changes the way programs (including dedicated servers and the Source engine) are downloaded, updated and stored.
Benefits
Players
The benefits to players are:
- Faster and smoother downloads
- Faster game boot times and map load times
- Easier distribution, installation, and management of mods
- Smoother dedicated server distribution and update rollover
Server administrators
Instead of a proprietary delivery protocol, SteamPipe uses HTTP, which allows datacenters hosting multiple servers to set up a caching HTTP proxy, necessitating only a single download of an update from Valve's servers.
Game developers
Game developers using SteamPipe can issue updates themselves; the previous system required manual intervention by Valve when an update was to be published.
LAN Caching
As SteamPipe now uses HTTP it allows not only datacenters hosting multiple servers to setup a caching but is also very useful for LAN's. Setting up a caching proxy can significantly reduce the amount of bandwidth required for multiple clients or servers to preform updates.
LANcache – Dynamically Caching Game Installs at LAN’s using Nginx is an example of how to setup caching proxy for SteamPipe as used at Multiplay's Insomnia Gaming Festival. steam-squid is a Docker image containing a Steam-optimised version of the Squid caching proxy for easy installation.
Downsides
Players
- Many Source SDK mods that use Half-Life 2 (and/or its Episodes) content that did not make the jump to the update are broken, this also includes some (but not all) Half-Life mods.
Fortunately, there are known fixes for many Half-Life 2 mods. Those fixes can be found here.. - With Source 2013 and SteamPipe, Half-Life 2 base content are no longer shared across all Source Engine games, as a result, most
 Source 2013 games (including third-party games) now contain duplicate copies of the Half-Life 2 base files (except in
Source 2013 games (including third-party games) now contain duplicate copies of the Half-Life 2 base files (except in 



 ), wasting storage drive space.
), wasting storage drive space.
 Warning:While the it is possible to point multiple games to the same VPK, not all VPKs with the same name are the same on all games! For example, the
Warning:While the it is possible to point multiple games to the same VPK, not all VPKs with the same name are the same on all games! For example, the 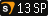 and
and 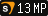 "hl2" VPKs are different from the VPKs actually used by
"hl2" VPKs are different from the VPKs actually used by  (which contains additional content and incompatible shaders from 20th Anniversary Update), the
(which contains additional content and incompatible shaders from 20th Anniversary Update), the  (including Team Fortress 2 branch) "hl2" VPKs are different from the other
(including Team Fortress 2 branch) "hl2" VPKs are different from the other 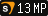 "hl2" VPKs.
"hl2" VPKs.
As of 2025: Both Half-Life 2 and Portal runs on updated version of Source 2013 Singleplayer (20th Anniversary Update), and the "hl2" files in both games are nearly identical enough that the game function correctly, while Source 2013 Singleplayer still runs on older version of Source 2013 Singleplayer branch from 2014 and ships with older version of "hl2" folder containing VPKs incompatible with both games. Workaround:Two options are such:
Workaround:Two options are such:- Use relative links to the VPKs (or folders) in gameinfo.txt, so they look something like this:
game "../Half-Life 2/hl2/hl2_textures.vpk"
- Use Symbolic links or Hardlinking VPKs (or folders) using programs such as Link Shell Extension (easier), or via Windows's
mklinkcommand; more info can be found here.
- Use relative links to the VPKs (or folders) in gameinfo.txt, so they look something like this:
- After the SteamPipe update,
 Half-Life: Source was not properly updated which resulted the game having more bugs and glitches, with graphical issues. This issue has never been fixed and Valve later instead de-listed the game from search (during Half-Life 25th Anniversary Update) in favor of promoting the original version instead, 10 years after the SteamPipe update was released.
Half-Life: Source was not properly updated which resulted the game having more bugs and glitches, with graphical issues. This issue has never been fixed and Valve later instead de-listed the game from search (during Half-Life 25th Anniversary Update) in favor of promoting the original version instead, 10 years after the SteamPipe update was released. - Source SDK Base 2007 fails to mount Half-Life 2: Episode Two assets properly, due to Valve mistakenly ships EP2 depot VPK files to Source SDK Base 2006. See Fixing VPK mounting for older Source SDK Bases for more information.
Developers
The Source SDK Launcher does not have support for ![]() Source 2013 games. Tools for games that used to be in the Source SDK Launcher must now be launched by going to "C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\[game name]\bin" (see example path below) then launching the .bat files (Example: Hammer.bat to launch Valve Hammer Editor).
Source 2013 games. Tools for games that used to be in the Source SDK Launcher must now be launched by going to "C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\[game name]\bin" (see example path below) then launching the .bat files (Example: Hammer.bat to launch Valve Hammer Editor).
Example path to SDK: ![]()
C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\SteamApps\common\Half Life 2\bin
Changes
- Downloads are performed using HTTP instead of a proprietary protocol.
- Data files are no longer placed into GCFs but directly into the file system. Games using Source engine before Left 4 Dead engine branch no longer shares Half-Life 2 base content between games.
- To counteract the performance issues with accessing many tiny files (the reason why GCFs were used in the first place), all Source games (prior to Left 4 Dead) distributed via SteamPipe now store their assets in VPK archives.
- Data generated before/during gameplay is no longer stored in user-specific subdirectories of SteamApps; instead, the common subfolder is used.
- Dedicated servers are using SteamCMD (a stripped-down version of the full Steam client).
See also
- GoldSource SteamPipe Directories for the list of directories used by GoldSource engine games
- IFileSystemV009 for the C++ interface used to access files through SteamPipe in GoldSource