3D model: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

TomEdwards (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Myzipis02139 (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A '''model''' is a collection of [[Wikipedia:Point (geometry)|points]], or "[[Vertex Editor|vertices]]", that form a 3D shape, or "[[mesh]]". The gaps between the points are usually filled with [[Wikipedia:Polygon (computer graphics)|polygons]], and these polygons are usually covered with a [[material]]. | A '''model''' is a collection of [[Wikipedia:Point (geometry)|points]], or "[[Vertex Editor|vertices]]", that form a 3D shape, or "[[mesh]]". The gaps between the points are usually filled with [[Wikipedia:Polygon (computer graphics)|polygons]], and these polygons are usually covered with a [[material]]. | ||
Models are used for almost every 3D object in Source that isn't a part of the underlying [[brush]] geometry. | Models are used for almost every 3D object in Source that isn't a part of the underlying [[brush]] geometry. [[NPC]]s, physics objects, guns, and even some buildings, to name but a few examples, are all models. | ||
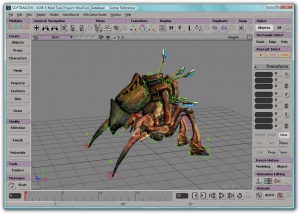
Models are created with programs external to the Source SDK; Valve recommend the [[XSI Mod Tool]], but there are [[Exporting a model|other options]]. The SDK tool [[studiomdl]] is used to convert the external program's files to the <code>[[MDL|.mdl]]</code> format that Source understands; see [[Model Creation Overview]] for more information. | Models are created with programs external to the Source SDK; Valve recommend the [[XSI Mod Tool]], but there are [[Exporting a model|other options]]. The SDK tool [[studiomdl]] is used to convert the external program's files to the <code>[[MDL|.mdl]]</code> format that Source understands; see [[Model Creation Overview]] for more information. | ||
Revision as of 09:02, 1 June 2008

A model being edited in the XSI Mod Tool.
A model is a collection of points, or "vertices", that form a 3D shape, or "mesh". The gaps between the points are usually filled with polygons, and these polygons are usually covered with a material.
Models are used for almost every 3D object in Source that isn't a part of the underlying brush geometry. NPCs, physics objects, guns, and even some buildings, to name but a few examples, are all models.
Models are created with programs external to the Source SDK; Valve recommend the XSI Mod Tool, but there are other options. The SDK tool studiomdl is used to convert the external program's files to the .mdl format that Source understands; see Model Creation Overview for more information.
World vs. View

A Half-Life 2 scene consisting entirely of world models.
- World Models
- Used by entities which appear in the 3D world. To ensure consistency an entity will normally enforce its own world model and not allow configuration in Hammer; the three main exceptions to this are
prop_static,prop_physics, andprop_dynamic. - View Models
- Used for hands and weapons that appear in the player interface. They are typically far more detailed than world models, but do not provide enough information to exist alongside them in the world.
Why use a model?
- Detail
- The number of vertexes on a model can be many, many times higher than on a world brush. Level of detail allows the extra detail to be bypassed when the model is too far away for it to be seen.
- Skeletal animation
- Detailed, efficient, believable animation can be achieved with a model. Walking, talking, running, jumping!
- Dynamism
- Unless specifically made to behave otherwise, a model's position, lighting, state and motion are all completely dynamic. They can go anywhere and do anything.
- Replication
- Every instance of a model is guaranteed to look the same. (Behaviour, however, depends on the entity!)
See also
- Category:World Models
- Half-Life Model Viewer
- Anatomy of a Model
- Model Creation Overview
- Category:Modeling
- MDL (Source Model file format)