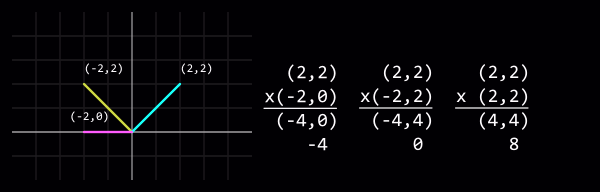Вектор
This page either contains information that is only partially or incorrectly translated, or there isn't a translation yet.
If this page cannot be translated for some reason, or is left untranslated for an extended period of time after this notice is posted, the page should be requested to be deleted.
Also, please make sure the article tries to comply with the alternate languages guide.
Вектор это C++ класс который представляет направление и имеет длину, начинающийся с нулевой точки объекта. Каждый вектор содержит три vec_t координаты:
- X +вперёд/-назад
- Y +лево/-право
- Z +вверх/-вниз
(1,20,5) означает 1 юнит вперёд, 20 юнитов влево и 5 юнитов вверх.
CUtlVector.Объявление
Vector vecMyVector = Vector(1,20,5);
- Класс вектора пишется как
Vector, а не vector. - Вы можете определять значения X, Y и Z отдельно.
- Префикс
vec(или простоv) определяет переменную как вектор.
Направление
У вектора нет направления; это определяется кодом, который используется.
In the vast majority of cases a vector will be interpreted as world axis aligned regardless of an entity's rotation, but there are few cases (e.g. applying physics forces), where they are considered object axis aligned.
There is no way of telling which interpretation will be used from the variable, so check for function comments when in doubt. Use VectorRotate() and VectorIRotate() to translate between alignments.
Использование
- Позиционирование
- Every entity's position ('origin') is stored as a vector relative to its parent: you are likely to be familiar with this idea already as Cartesian grid coordinates. See
GetAbsOrigin()for more details. - Movement
- An entity attempts to move the length of its velocity vector once per second.
- Collision Traces
- A Traceline or -hull is fired from one point to another, detecting what it "hits" along its path.
Операции
All vectors in an operation must have the same origin for the result to make sense. Whether a local or absolute origin is used depends on what you're trying to achieve.
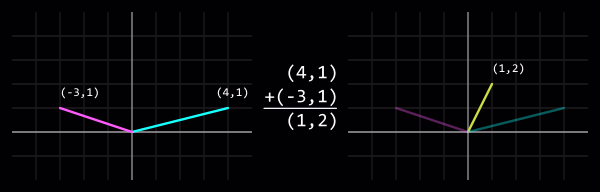
Сложение
Сложение двух (или более) векторов складывает их значения. Вы уже складывали векторы, если толкали что либо двумя руками!
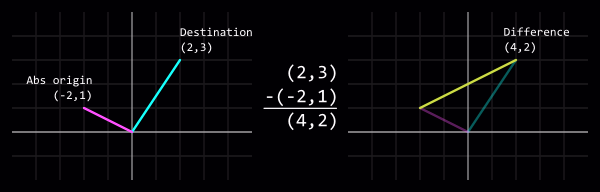
Вычитание
Вычитание одного вектора из другого это разница между ними - другими словами, как добраться из первого вектора в другой.
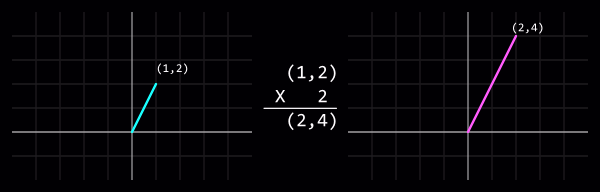
Умножение
Скалярное
Умножение или деление вектора скалярно (то есть на int или float) изменит длину вектора не изменяя его направления.
VectorNormalize() чтобы быстро это сделать.Dot product
Multiplying two vectors then adding the result's ordinates produces a dot product, which when both vectors have been normalised is equal to the cosine of the angle between the two vectors.
One use of a dot product is to tell how closely the two vectors align. +1 means a match, 0 means they are perpendicular to each other, and -1 means they are opposed.
This code calculates a dot product with the aid of Source's various helper functions:
Vector vecTarget = pTarget->GetAbsOrigin() - GetAbsOrigin(); // Get local vector to target
VectorNormalize(vecTarget); // Normalisation needs to be done beforehand
Vector vecFacing;
AngleVectors(GetLocalAngles(),&vecFacing); // Convert facing angle to equivalent vector (arrives normalised)
float result = DotProduct(vecTarget,vecFacing); // Get the dot product
if (result > 0)
Msg("pTarget is in front of me!\n");
Cross product
A cross product is a vector perpendicular to two input vectors. It's used to extrapolate a third dimension from just two: the cross product of a vector pointing down the X-axis and a vector pointing down the Y-axis is a vector pointing down the Z-axis.
The equation is fiddly and doesn't have to be learnt; just use CrossProduct(vecA,vecB,&vecResult). There generally isn't any need to normalise the input vectors. Most modders will likely only use cross products rarely, if ever - but if required, be aware that a moderate amount of math is required to properly understand this operation.
Поворот
Для поворота вектора нужна матрица, это нельзя сделать также легко как умножение. К счастью не нужно в это вникать: можно просто вызвать VectorRotate(Vector in, QAngle in, Vector& out).
Специальные вектора
в Source есть два вида специальных векторов:
vec3_origin- Vector(0,0,0).
vec3_invalid- Для неверных векторов
Member functions
Length
vec_t Length()vec_t LengthSqr()Length()returns the vector's length in units. It's faster to useLengthSqr()and square the other value being compared.bool IsLengthGreaterThan(flValue)bool IsLengthLessThan(flValue)- Helpers that perform fast length checks using
LengthSqr(). void Zero()- Sets all elements to 0.
Direction
void Init(vec_t X, Y, Z)- Quickly set an existing vector's ordinates.
void Random(vec_t minVal,vec_t maxVal)- Randomises all three ordinates within the given range.
void Negate()- Reverses the vector's direction without affecting its length.
Vector Max(vOther)Vector Min(vOther)- Clamps the vector's ordinates either above or below the given values. The ordinates won't stay in proportion (i.e. direction might change).
Comparison
vec_t DistTo(vOther)vec_t DistToSqr(vOther)- Returns the distance between the current vector and
vOtheras a scalar. As ever, the squared flavour is faster. vec_t Dot(vOther)- Returns the dot product of the current vector and
vOther. Vector Cross(vOther)- Returns the cross product of the current vector and
vOther. bool WithinAABox(vecBoxmin,vecBoxmax)- Tests whether the Vector ends within the given box. Box min/max values are local to the Vector.
Casts
Vector2D AsVector2D()- Casts to Vector2D.
vec_t Length2D()vec_t Length2DSqr()- As their standard equivalents, but ignoring the Z-axis.
Base()- Casts to vec_t*, basically the same as &vec.x or (float*)&vec.
Helper functions
These globals are all available through cbase.h.
float VectorNormalize(vec)- Divides the vector by its length, normalising it. Modifies the Vector and returns the old length.
vec_t DotProduct(vecA,vecB)- See #Dot product.
void CrossProduct(vecA,vecB,vecResult)- See #Cross product.
void VectorTransform(Vector in1, matrix3x4_t in2, Vector out)- See matrix3x4_t.