Particle position
Particle position initializers decide the location(s) at which particles are created.
Position Along Path Random
See Position Along Path Sequential.
Position Along Path Sequential
See Position Along Path Sequential.
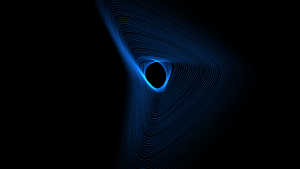
Position Along Epitrochoid
Particles are created at a point in the circumference of a circle spinning along another fixed circle. (Known as an "epicycle".)
- control point number
- The control point to create the epitrochoid.
- first dimension 0-2 (-1 disables)
- second dimension 0-2 (-1 disables)
- The orientation of the circles as if they existed in 2D space.
- local space 0/1
- Whether to create the epitrochoid in the world, or in the particle systems local space.
- offset from existing position
- Apply the epitrochoid to other position initializers.
- particle density
- How fast to map the particles to the epitrochoid.
- point offset
- The amount to offset radius 2 from radius 1.
- radius 1
- The size of the fixed circle.
- radius 2
- The size of the spinning circle.
- scale from conrol point (radius 1/radius 2/offset)
- [Todo]
- use particle count instead of creation time
- Use particle count to determine the particles spawn position along the epitrochoid. (Useful for emit_instantaneously)
Position Along Ring
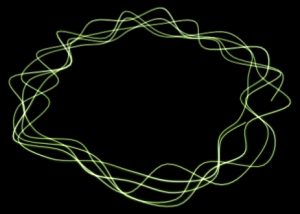
Particles are created the edge of a circle. The circle can be thickened to a 3D torus.
- control point number
- The ring centres on this control point.
- even distribution
- Creates particles at regular intervals around the ring. Normally their position is random.
- even distribution count
- The number of locations at which particles are created. Ignored if even distribution is disabled.
- initial radius
- Number of units from the control point to the ring line.
- max initial speed
- min initial speed
- Gives particles an initial velocity pointing away from the control point.
- XY velocity only
- Particles with initial speed will not have any velocity in the Z axis. Only relevant if thickness is used.
- Override CP
- A control point from which to take override values for this operator.
- Radius = X
- Thickness = Y
- Initial speed = Z
- pitch
- roll
- Rotates the ring. Very hight values are required for some reason; 5150 is roughly a 90° twist.
- thickness
- Particles can spawn up to this far away from the ring line.
Position From Chaotic Attractor
Spawns particles along a random pattern starting at a single point using a mathematical equation known as the Clifford Pickover Attractor. (Works especially well with ropes)
- Relative Control point number
- Create the pattern at this control point.
- Pickover A Parameter
- Pickover B Parameter
- Pickover C Parameter
- Pickover D Parameter
- The values to use in the calculation of the new particle positions.
- Scale
- Multiply the final positions by this factor.
- Speed Max
- Speed Min
- Gives particles an initial velocity pointing away from the control point.
- Uniform speed
- Normalizes the speed to accurately represent the generated pattern.
Position from Parent Cache
Seems to use collision mode 2 from its parent particle to spawn particles at the first found plane in the -X direction
- Local Offset Max
- Local Offset Min
- vector offset for the spawn positions
- Set Normal
- [Todo]
Position From Parent Particles
Spawn particles at the position of existing ones in the parent
- Inherited Velocity Scale
- How much of the velocity of the parent particles each child particle inherits.
- Particle Increment Amount
- The amount of particles to spawn before spawning at a new parent particle in the particle list. (0 will spawn the children particles at a single parent particle, until the parent particle is killed and a new is created.)
- Random Parent Particle Distribution
- The creation positions of the particles will be randomly selected from current active parent particles.
Position In CP Hierarchy
Particles creation positions "crawl" along a chain of control points. Seems quite buggy.
- growth time
- How long it takes for particles to travel from the first CP to the last.
- distance_bias
- distance_bias_absolute_value
- [Todo]
- use highest supplied end point
- [Todo]
- start control point number
- end control point number
- bulge
- bulge control
- mid point position
- See Position Along Path Sequential.
Position Modify Offset Random
Moves particles after their initial position has already been calculated.
- offset max
- offset min
- The range within which positions will be offset. Displayed as a box in the preview window.
- offset proportional to radius
- Multiplies the offset values by the radius of each particle.
- offset in local space
- Whether the min/max values should be considered relative to the world or to the control point they were emitted from.
 Bug:The helper box is displayed incorrectly when this property is active.
Bug:The helper box is displayed incorrectly when this property is active.
Position Modify Place On Ground
Tries to move particles to the first solid surface beneath them.
This initializer has the same properties as the Movement Place On Ground operator.
Position Modify Warp Random

Scales the position of each particle. This can be used to contort the emission shape, and is how the elongated rings seen in Portal are created. Initial velocities are also warped.
- warp min
- warp max
- The warping factor in three dimensions.
1 1 1results in no warping. - control_point_number
- The control point relative to which warp will be applied.
- warp transition time
- Treats the min/max as start and end sizes for a transition that takes place over this many seconds.
- warp transition start time
- When the transition will start.
- reverse warp
- Makes the transition run backwards.
Position on Model Random
Creates particles within a control point's associated entity. This works with both model entities and brush entities.
- control_point_number
- The control point to get an entity from.
- desired hitbox
- The hitbox index within which to create particles, if the entity uses a model. Use -1 to target all of them.
- direction bias
- Biases which parts of the hitbox (or whole model if all of them are active) receive the most particles.
0 0 10will ensure that almost all particles spawn in the upper half.Todo: Precise meaning of the value. - force to be inside model
- Tries to ensure that particles aren't created outside the model's surface.
 Note:Particles generated more than a few units away will not be affected.
Note:Particles generated more than a few units away will not be affected. - model hitbox scale
- Scale the size of each hitbox by this factor (for particle placement only).
Position Within Box Random
Particles are positioned at a random location inside a box.
- control point number
- The control point to centre the box on.
- min
- max
- Defines the far corners of the box.
- use local space
- Applies the control point's rotation and local offset (if any) to the box.
Position Within Sphere Random
Particles are positioned at random inside a sphere or hollow shell, and are optionally given an initial velocity.
- control_point_number
- The control point to centre the sphere on.
- distance_min
- distance_max
- The nearest and farthest distance from the control point at which to place particles.
- distance_bias
- The likelihood of particles being created in each axis (X, Y, Z). Setting any of the three numbers to 0 will flatten the sphere in that direction, while setting to 10 will lead to roughly 10 times as many particles near the far ends of that axis. Useful for creating discs, rings, and polar effects.
- distance_bias_absolute_value
- If any axis is non-zero, all particles will be eliminated from that hemisphere. Use distance_bias to alter the effect (e.g. a negative value will flip the hemisphere from one side to the other).
- bias_in_local_system
- Sets whether the biasing values should be interpreted locally to the central control point. If they are, then the CP's rotation affects the outcome of the initializer.
- speed_min
- speed_max
- Particles will be initialised with a velocity that repulses them from the centre of the sphere at this many units per second.
 Note:A Movement Basic operator is required for this to have any visible effect.
Note:A Movement Basic operator is required for this to have any visible effect. - speed_random_exponent
- A factor for how likely the minimum speed is to be applied.
- 0 means that all particles will move at maximum speed
- 1 means an even spread
- Above 1 makes particles increasingly likely to move at minimum speed
- speed_in_local_coordinate_system_min
- speed_in_local_coordinate_system_max
- In addition to movement away from the central control point, you can initialise particles with a random velocity. As the name suggests, these directions are always relative to the central control point's rotation.