Es/VGUI Documentation
Descripción general
La libreria VGUI2 (vgui2.dll) es propiedad de una interfaz gráfica de usuario (GUI) proporcionada por el Source Engine. Todas las aplicaciones Source & Steam usan VGUI para presentar ventanas, dialogos o menus. La arquitectura de objetos es jerarquica y todos los elementos implementados son controlados desde las clases base del VGUI. El sistema de entradas del teclado y el ratón es conducido por eventos y bastante similar a otras librerias GUI (como ![]() Java Swing o
Java Swing o ![]() Formularios .NET). Las implementaciones para los elementos GUI más comunes como botones, campos de texto o imagenes, son proporcionadas por la libreria de controles VGUI (
Formularios .NET). Las implementaciones para los elementos GUI más comunes como botones, campos de texto o imagenes, son proporcionadas por la libreria de controles VGUI (vgui_controls.lib). Además de dibujar elementos GUI y procesar entradas, VGUI tanbién controla la localización para la presentación de testo en el lenguaje preferido.
Todos los VGUI base de las cabeceras de la interfaz se encuentran en \public\vgui\, los elementos de control son definidos en \public\vgui_controls\.
Como autor de mods lo más probable es que uses VGUI en el proyecto client.dll para mostrar los menús, elementos HUD o para presentaciones dentro del juego (en weapons o ordendaores, etc). La clase básica de la que derivan todos los elementos VGUI es vgui::Panel, que define un area en tu pantalla que tiene un tamaño específico y una posición, puede dibujarse a si misma y procesar eventos de entrada. Las ventanas de dialogo, campos de texto y botones son todos paneles VGUI en relación jerarquica padre-hijo. El primer panel es el panel raiz y es proporcionado por el motor Source. El panel raiz del cliente cubre la pantalla entera, pero no muestra nada. Incluso aunque pudieras usar el panel raiz del cliente, la mayoria de paneles de cliente usan el panel compartido BaseViewport como padre ( g_pClientMode->GetViewport() ).
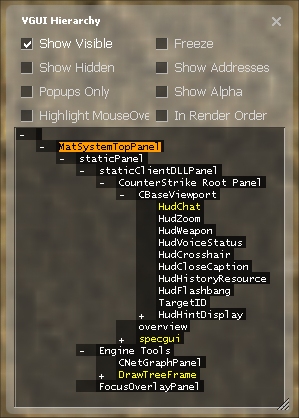
Este diagrama muestra una parte de la jerarquía del panel del cliente. Una flecha del panel a al panel b significa que a es padre de b .
Para navegar a través de la jerarquía del panel VGUI durante el tiempo de ejecución, puedes abrir la herramienta VGUI Hierarchy ejecutanto el comando vgui_drawtree 1 en la console de desarrollo. Todos los paneles están listados en un TreeView expandible.
Los nombre de los paneles están coloreados:
| blanco | El Panel es visible |
| gris | El Panel esta oculto |
| amarillo | Panel Popup (Frame) |
| verde | El Panel tiene el foco |
Las siguientes opciones están disponibles:
| Show Visible | Lista todos los paneles visibles. |
| Show Hidden | Lista todos los paneles ocultos. |
| Popups only | Lista solo los paneles Popup (Frames) |
| Highlight Mouse Over | Los paneles están destacados con un borde coloreado cuando mueves el ratón sobre el. El árbol de paneles se expanderá para mostrar el panel actual. |
| Freeze | Bloquea el TreeView actual. |
| Show Addresses | Muestra las direcciones de memoria de los paneles. |
| Show Alpha | Muestra el valor alpha del panel, 0 = translucido, 255 = opaco |
| In Render Order | Muestra un árbol de paneles en orden de presentación. |
La Clase Panel
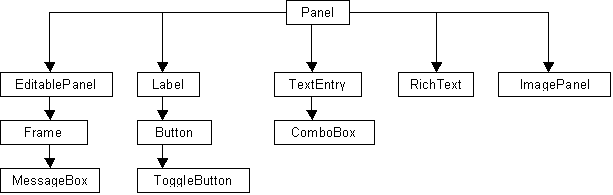
La clase VGUI Panel es la clase base para, alrededor de 50 elementos de control diferentes, que son definidor en \public\vgui_controls\. Los archivos de cabecera normalmente proporcionan una buena documentación sobre las características y comportamientos del control. El siguiente diagrama muestra la jerarquía de clase para algunos elementos comunmente utilizados:
Desde que todas las clases VGUI derivan de la clase Panel, deberemos prestar una mayor atención a las funciones y propiedades esenciales de sus miembros.
El constructor más habitualmente utilizado para crear un panel es Panel(Panel *parent, const char *panelName), desde que cada panel necesita un panel-padre, este pertenece a un único nombre en su nivel jerarquico. Una vez un panel es creado, puedes hacerlo visible o ocultarlo de nuevo con SetVisible(bool state).
VGUI mantiene un identificador para cada nuevo grupo, que se utiliza para tratar globalmente un panel sin pasar punteros. Muchos eventos de funciones de mensajería usan ese identificador VPANEL para reconocer paneles fuente y objeto. Para conseguir el identificador único VPANEL de un panel, llama a GetVPanel().
Para establecer la posición y el tamaño de un panel usa las funciones miembro SetPos(int x,int y) y SetSize(int wide,int tall). EL tamaño siempre en pixeles y no se escala automáticamente con aumento de resoluciones. La posición es siempre relativa al panel - padre dado, donde (0,0) es la esquina superior izquierda.
Para hacer una iteración a través de la jerarquía de paneles usando un determinado panel como punto de inicio, debes conseguir el panel-padre llamando GetParent() o GetVParent() para tomar el identificadr correspondiente VPANEL. Por supuesto, un panel puede tener solo un panel-padre, pero múltiples paneles-hijo (sub panels, botones, elementos de lista, etc). GetChildCount() devolverá el número total de hijos, pudiendo ser cada uno consultado con GetChild(int index).
Si un panel debe reaccionar a eventos de entrada como una tecla presionada o un click del ratón, las funciones virtuales OnEvent() como OnMousePressed(MouseCode code) o OnKeyCodePressed(KeyCode code) deben ser overrideadas. Los eventos de entrada de ratón y teclado pueden ser activados / desactivados para un panel, usando SetMouseInputEnabled(bool state) o SetKeyBoardInputEnabled(bool state).
Otra útil función virtual a overridear es OnThink() que es llamada cada vez que el panel es repintado. En ocasiones, esto es demasiado y querrás actualizar o chequear el exstado del panel menos a menudo. Entonces puedes conectar con OnTick() llamada frecuentemente en un intervalo de tiempo ajustable. Pero debe ser dicho que VGUI debería llamar OnTick() para un panel dado y cuan a menudo, esto se hace con ivgui()->AddTickSignal(VPANEL panel, int intervalMilliseconds).
Windows & popups
A Panel as described above is always a 100% sub area of its parent panel, its position is always a fixed relative offset and can only be changed by code. Also it draws itself only inside the parent region, if you move a VGUI element outside the parent panel, it will be clipped. This is fine for adding control elements, images or text fields to a panel, but wouldn't allow independent pop-up windows or dialog boxes the user can move around, resize and minimize. Therefore, VGUI panels have the MakePopup() function which decouples a panel from is parent rendering and makes it a new, independent window. Still it belongs to a parent panel and becomes invisible if the parent does.
In most cases you won't call MakePopup() by yourself but use the Frame class instead. The Frame class encapsulates all common GUI windows features like title bar, system menu (close, minimize, maximize), dragging, resizing, focus and layout management.
Here a short example how to open a frame and activate it. Note that the frame will delete itself once the user closes the Frame or the Close() function is called (just make sure that your stuff is cleaned up in the destructor).
Frame *pFrame = new Frame( g_pClientMode->GetViewport(), "MyFrame" );
pFrame->SetScheme("ClientScheme.res");
pFrame->SetSize( 100, 100 );
pFrame->SetTitle("My First Frame", true );
pFrame->Activate(); // set visible, move to front, request focus
If a Frame is resized, the virtual function PerformLayout() is called so the frame can rearrange its elements to fit best for the new size. The current Frame position and size can also be locked with SetMoveable(bool state) and SetSizeable(bool state).
Event messaging
VGUI panels communicate via a message system to signal state changes or events to parents or children (or any other panel). Messages are not sent directly (e.g. by calling a panel listener function), rather they are handed over to VGUI which delivers them to the target panel. Thus beside the message content, a sender and a receiver panel must be specified as VPANEL handles. VGUI sends event messages to inform panels about changes or events (mouse moved, input focus changed etc).
The message name and content is specified using a KeyValues object (\public\KeyValues.h). The KeyValues class is a very generic and flexible structure to store data records containing strings, integer or float numbers. A KeyValues object has a name and a set of data entries. Each entry has a unique key name and corresponding value. KeyValues also allow creating hierarchical structures using sub keys, though most VGUI messages are flat data records. KeyValues don't have data/type definitions or similar, so you can add or remove entries of any type as you like. Thus sender and receiver must both know the internal structure (e.g. key names, types and their meaning) of a KeyValues message object to communicate successfully. Here some sample code how to use KeyValues in general:
// create a new KeyValues Object named "MyName"
KeyValues *data = new KeyValues("MyName");
// add data entries
data->SetInt( "anInteger", 42 );
data->SetString( "aString", "Marvin" );
// read data entries
int x = data->GetInt("anInteger");
Con_Printf( data->GetString("aString") );
// destroy KeyValues object again, free data records
data->deleteThis();
To send a message you can call the Panel member function PostMessage(...) or directly ivgui()-> PostMessage(...). The name of the KeyValues object is also the message name used for later dispatching. VGUI will call the target panel's OnMessage(...) function, which will dispatch the message to a previous defined message handler. A panel can register new message handlers with one of the MESSAGE_FUNC_* macros, which adds a handler function to the message map. Never override OnMessage(...) to handle new messages, always use a macro. Please note that when you use the macro MESSAGE_FUNC_* only those specific messages will be thrown to your function. If you want to catch the newLine (ENTER) message from a txtEntry element you will use MESSAGE_FUNC_PARAMS( NewLineMessage, "TextNewLine",data). NewLineMessage is function to call, "TextNewLine" means all messages who's names are "TextNewLine" will be redirected and finally data is the input that will be passed to your function. In this case NewLineMessage will look like this void MyParentPanel::NewLineMessage (KeyValues *data).
class MyParentPanel : public vgui::Panel
{
...
private:
MESSAGE_FUNC_PARAMS( OnMyMessage, "MyMessage", data );
}
void MyParentPanel::OnMyMessage (KeyValues *data)
{
const char *text = data->GetString("text");
}
The sending panel creates a KeyValues object, adds message parameters and sends the message (to its parent in this case). The KeyValues object is destroyed by VGUI after it has been processed.
void MyChildPanel::SomethingHappened()
{
if ( GetVParent() )
{
KeyValues *msg = new KeyValues("MyMessage");
msg->SetString("text", "Something happened");
PostMessage(GetVParent(), msg);
}
}
Using PostMessage() the sending panel must address a single, specific target, which means that all other panels interested in a state change must be known and addressed individually. To avoid hard coding these dependencies, panels have a public event system called action signals. A panel fires generic events with PostActionSignal(KeyValues *message) and interested panels can register as listeners for these signals with AddActionSignalTarget(Panel *target). These action signals are widely used by VGUI controls, for example messages like "TextChanged" fired by class TextEntry or "ItemSelected" used by class ListPanel. All action signal messages contain a pointer entry "panel" that points to the sending panel.
The example from above using action signals would need the parent panel to register as a listener, preferably in the constructor after the child panel has been created. The child panel just uses PostActionSignal() instead of PostMessage():
MyParentPanel::MyParentPanel()
{
...
m_pChildPanel->AddActionSignalTarget( this );
}
void MyParentPanel::OnMyMessage (KeyValues *data)
{
const char *text = data->GetString("text");
Panel *pSender = (Panel *) data->GetPtr("panel", NULL);
}
void MyChildPanel::SomethingHappened()
{
KeyValues *msg = new KeyValues("MyMessage");
msg->SetString("text", "Something happened");
PostActionSignal ( msg );
}
To catch the return/enter key from a txtEntry element use this.
class MyParentPanel : public vgui::Panel
{
...
private:
MESSAGE_FUNC_PARAMS( OnMyMessage, "NewLineMessage", data );
}
MyParentPanel::MyParentPanel()
{
...
m_pChildPanel = new vgui::TextEntry( this, "txtEntry" );
m_pChildPanel->AddActionSignalTarget( this );
m_pChildPanel->SendNewLine(true); // with the txtEntry Type you need to set it to pass the return key as a message
}
void MyParentPanel::NewLineMessage (KeyValues *data)
{
// when the txtEntry box posts an action signal it only sets the name
// so it is wise to check whether that specific txtEntry is indeed in focus
// Is the Text Entry box in focus?
if (m_pChildPanel->HasFocus())
{
// We have caught the message, now we can handle it. I would simply repost it to the OnCommand function
// Post the message to our command handler
this->OnCommand("Submit");
}// End HasFocus()
}
// Dawid Joubert 2006-02-11
A commonly used action signal is the "Command" message, since no message handler needs to be installed. Panels just need to derive the virtual Panel function OnCommand(const char *command) and check for the correct command string. The "Command" message is used by all Button classes and is fired whenever the button is pressed. Here is the example from above using the Command message:
class MyParentPanel : public vgui::Panel
{
...
protected:
virtual void OnCommand(const char *command);
}
MyParentPanel::MyParentPanel()
{
...
m_pChildPanel->AddActionSignalTarget( this );
}
void MyParentPanel::OnCommand(const char *command)
{
if (!stricmp(command, "SomethingHappened"))
{
DoSomething ();
}
else
{
BaseClass::OnCommand(command);
}
}
void MyChildPanel::SomethingHappened()
{
KeyValues *msg = new KeyValues("Command");
msg->SetString("command", "SomethingHappened");
PostActionSignal ( msg );
}
Schemes
A VGUI scheme defines the general "look & feel" of your panels by specifying used colors, fonts & icons of control elements. Schemes are defined in resource files, for example hl2\resource\clientscheme.res. A new panel inherits by default the scheme settings used by its parent. The VGUI scheme manager can load a new scheme with LoadSchemeFromFile(char *fileName, char *tag) which returns HScheme handle. To make a panel using a loaded VGUI scheme call the panel member function SetScheme(HScheme scheme).
Schemes set the general look of panel elements, but they don't arrange specific control elements of your panel. One way of adding elements to your panel is by doing that in source code. You can create them (usually in the constructor of the parent panel) and set properties like size and position manually using the panel member functions. This will become quite complex and time-consuming for larger dialogs with lots of control elements.
The most common way to define the layout of your panel elements is to describe all elements in an external resource file like hl2\resource\UI\classmenu.res (a KeyValues text file). When the parent panel is created, this file is loaded and executed with LoadControlSettings(char *dialogResourceName). Do note, however, that this function is only defined for EditablePanel (or an EditablePanel derivative such as Frame). In this resource file each control element is defined in a separate section. A typical control definition looks like this:
"MyControlName"
{
"ControlName" "Label" // control class
"fieldName" "MyControlName" // name of the control element
"xpos" "8" // x position
"ypos" "72" // y position
"wide" "160" // width in pixels
"tall" "24" // height in pixels
"visible" "1" // it's visible
"enabled" "1" // and enabled
"labelText" "Hello world" // show this text
"textAlignment" "west" // left text alignment
}
Each control property has a key name and a value. Properties defined by the base class Panel are available for all controls (like xpos, ypos, wide, tall etc). A list of all available key names is returned by the panel member function GetDescription(). Derived panel classes may add new fields for their specific properties. Processing these new fields must be handled by overriding the virtual function ApplySettings(KeyValues *inResourceData). Here you can also lookup how values for an existing control property are interpreted.
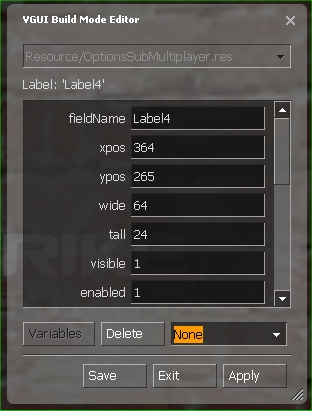
Build mode
An even simpler way to edit panel and control layouts is the VGUI Build Mode. This allows you to modify and save the layout of a panel resource file while the application is running. To edit a panel, just start the game and open this panel, so it gets the input focus. Then press SHIFT+CTRL+ALT+B to open the VGUI Build Mode editor. In Build Mode you can easily rearrange existing elements and change their control properties (press 'Apply' to update changes). To add a new control element, just choose the desired class from the combo-box on the lower right side and an empty control object of that class will be place in your panel for further editing. To save the current layout in the associated resource file press the 'Save' button (make sure the resource file is not write-protected).
Drawing & surfaces
Using schemes and control properties you can change the general appearance and layout of existing controls, but it doesn't allow you to create completely new elements. To change the appearance of a panel you have to override the two virtual functions Panel::Paint() and Panel::PaintBackground(). In these functions you can use drawing functions provided by the ISurface interface to place lines, rectangles, text, images etc. When updating the screen, VGUI calls first PaintBackground() and then Paint() for each panel and its children panels recursively. Drawing coordinates are relative to the panel you draw in. Here same example code how to draw a red box in the upper left corner:
void MyPanel::Paint(void)
{
BaseClass::Paint();
surface()->DrawSetColor( 255, 0, 0, 255 ); //RGBA
surface()->DrawFilledRect( 0, 0, 20, 20 ); //x0,y0,x1,y1
}
To draw text on a panel surface you need to set the used font first. Fonts have names like "DefaultSmall" and their properties like True-Type-Font, size and weight are defined in scheme resource files. The font handle can be retrieved by calling GetFont("Name") of the current panel scheme, then the surface can be told to use it as the current font. After setting the color and position for the next text output, the text itself must be passed as wide char string (Unicode) to DrawPrintText(...). This text will not be printed as it is and not localized anymore, so localization tokens must be translated beforehand.
void MyPanel::Paint(void)
{
wchar_t *pText = L"Hello world!"; // wide char text
// get the right font handle for this scheme
vgui::IScheme *pScheme = vgui::scheme()->GetIScheme(GetScheme());
vgui::HFont hFont = pScheme->GetFont( "DefaultSmall" );
surface()->DrawSetTextFont( hFont ); // set the font
surface()->DrawSetTextColor( 255, 0, 0, 255 ); // full red
surface()->DrawSetTextPos( 10, 10 ); // x,y position
surface()->DrawPrintText( pText, wcslen(pText) ); // print text
}
To draw a texture or image, VGUI has to load the texture from disk once (panel constructor) and generate a corresponding texture ID. This texture ID is then used as reference when drawing the texture. Here an example how to load and draw the texture "\materials\your_folder\mylogo.vmt":
MyPanel::MyPanel(void)
{
//Do _not_ forget CreateNewTextureID(), it gave me a headache for a week
m_nTextureID = vgui::surface()->CreateNewTextureID();
vgui::surface()->DrawSetTextureFile( m_nTextureID, "vgui/your_folder/mylogo" , true, false);
}
void MyPanel::Paint(void)
{
vgui::surface()->DrawSetTexture( m_nTextureID );
vgui::surface()->DrawSetColor(50,50,50,100);
vgui::surface()->DrawTexturedRect( 0, 0, 100, 100 );
}
Proportionality
Coordinate values that you specify in configuration files are relative to a 640x480 resolution if SetProportional(true) is called before a file is loaded (which, by default, it is). These values will be scaled to the correct size no matter what the user's current resolution may be. For example, a "tall" value of 120 will always mean the panel takes up 1/4th the height of the screen, and an "x" value of 320 means that the panel's left edge will always be centered.
c-<wide/tall> in your xpos and ypos values to center an element on-screen at different aspect ratios.However, sometimes you will need to calculate coordinates for custom painting and forgo the luxury of configuration files. The problem is that values that you specify in code are relative to the user's native resolution, which may or may not be the same as the current game resolution (thus rendering surface()->GetScreenSize() useless). The solution to this problem is to use scheme()->GetProportionalScaledValue(). This allows you to specify a coordinate on the 640x480 resolution and have it be remapped to the current resolution.
Localization
VGUI text elements support automatic localization for the preferred user language. Lets assume a text label should show "Hello world!" then you could set this text directly with SetText( "Hello World."). But if the user would choose a different language than English this label would still show the English text. Therefore you should always use localization tokens to tell VGUI to translate the token into user language, in this example SetText( "#MyMod_HelloWorld"). Tokens are strings starting with the hash sign '#' as control character to tell VGUI that this is not plain text.
VGUI keeps a global translation table to map tokens to plain text representation. These translation tables are loaded from resource files, where each file has an extra copy for every supported language (e.g. \resource\hl2_english.txt, \resource\hl2_german.txt).
A new token definition for your game would look like this:
In mymod_english.txt:
"MyMod_HelloWorld" "Hello world."
In mymod_german.txt:
"MyMod_HelloWorld" "Hallo Welt." "[english]MyMod_HelloWorld" "Hello world."
If your game folder is named "mymod" the Source engine will automatically load the correct translation file (/resource/gamedir_language.txt). You can load additional translation files using the ILocalize interface function AddFile(...).
You can use the ILocalize interface also to manually translate a token into current user language, e.g. vgui::localize()->Find("#MyMod_HelloWorld"). This function returns the translation as a 16-bit wide char string (Unicode).
VGUI uses Unicode for all text representation to support languages that use more then the 255 ASCII characters, like Chinese or Russian. Language resource files are encoded as Unicode. Note that the files will not be loaded properly unless they are specifically saved with proper Unicode encoding. To convert strings between ANSI ASCII and Unicode during runtime you can used the ILocalize interface functions ConvertANSIToUnicode(...) and ConvertUnicodeToANSI(...). Also a very useful function is ConstructString(...) which is basically like sprintf(...) for Unicode strings.
See also
Tutorials
Template:Otherlang:es Template:Otherlang:es:ru, Template:Otherlang:es:en