Primitive: Difference between revisions
m (grammar) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{{note|Another option that may cause problems can be found under the Tools/Options/General tab: 'Stretch arches and toruses to fit original bounding rectangle.' This means any arches or tori you create will fill the box you drew. If turned off it will consider that box as defining the circle the arch or torus is drawn from.}} | {{note|Another option that may cause problems can be found under the Tools/Options/General tab: 'Stretch arches and toruses to fit original bounding rectangle.' This means any arches or tori you create will fill the box you drew. If turned off it will consider that box as defining the circle the arch or torus is drawn from.}} | ||
===Simple=== | |||
=== | ====Block==== | ||
== | |||
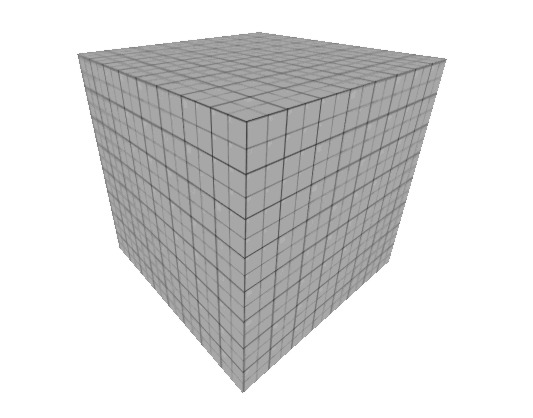
The block, a basic cube, is the most used object when mapping in Hammer. | The block, a basic cube, is the most used object when mapping in Hammer. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 13: | ||
[[Image:primitive_block.jpg]] | [[Image:primitive_block.jpg]] | ||
===Cylinder=== | ====Cylinder==== | ||
A cylindrical brush created with a specified number of sides. | A cylindrical brush created with a specified number of sides. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 19: | ||
[[Image:primitive_cylinder.jpg]] | [[Image:primitive_cylinder.jpg]] | ||
===Sphere=== | ====Sphere==== | ||
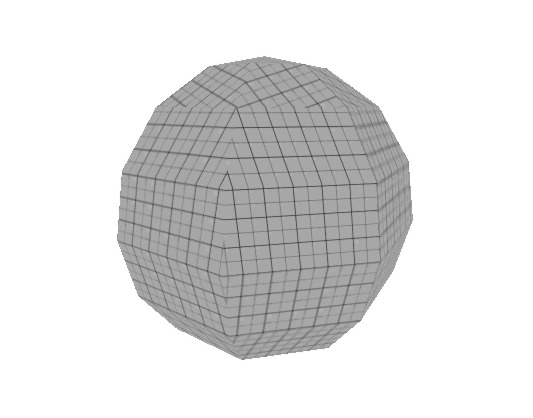
The sphere is a rather complicated piece of geometry, so it would be wise to be careful with the number of faces you give the sphere. | The sphere is a rather complicated piece of geometry, so it would be wise to be careful with the number of faces you give the sphere. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 25: | ||
[[Image:primitive_sphere.jpg]] | [[Image:primitive_sphere.jpg]] | ||
===Spike=== | ====Spike==== | ||
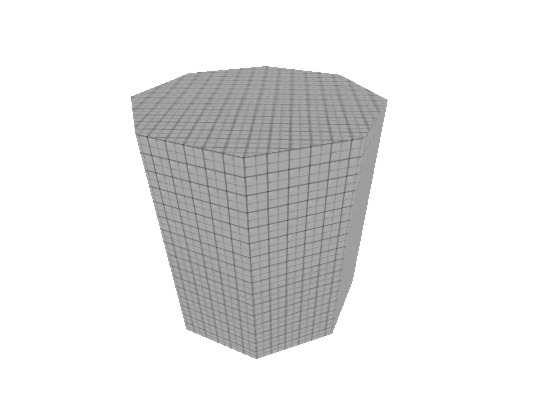
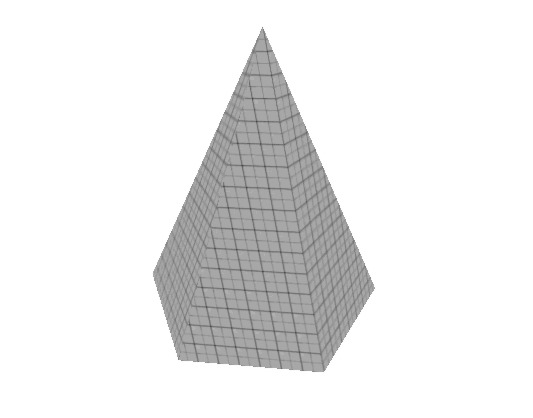
Like the cylinder, but all the top vertices come to 1 central point. | Like the cylinder, but all the top vertices come to 1 central point. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 31: | ||
[[Image:primitive_spike.jpg]] | [[Image:primitive_spike.jpg]] | ||
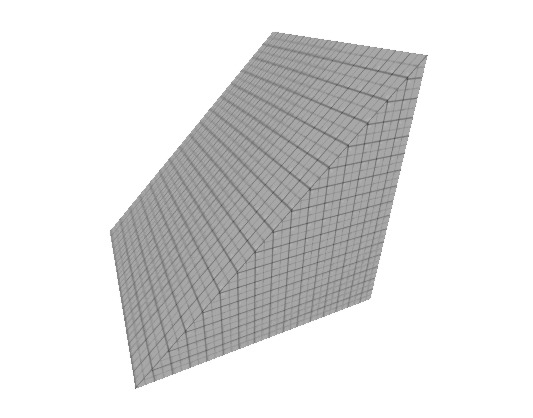
=== | ====Wedge==== | ||
The wedge is basically a triangular prism. | |||
[[Image:primitive_wedge.jpg]] | |||
===Complex=== | |||
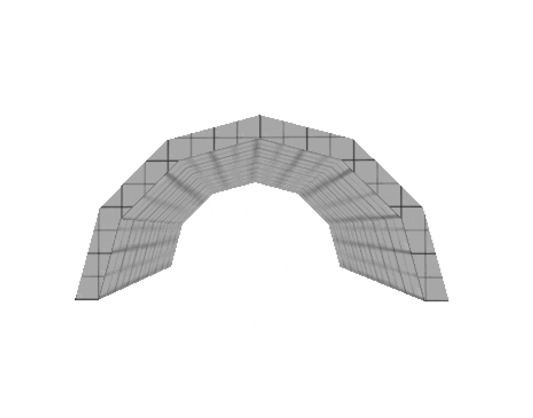
====Arch==== | |||
This creates a basic arch as defined by the [[Hammer Arch Properties | Arch Tool]]. Multiple blocks slightly rotated will be created within 1 group. | |||
[[Image:primitive_arch.jpg]] | |||
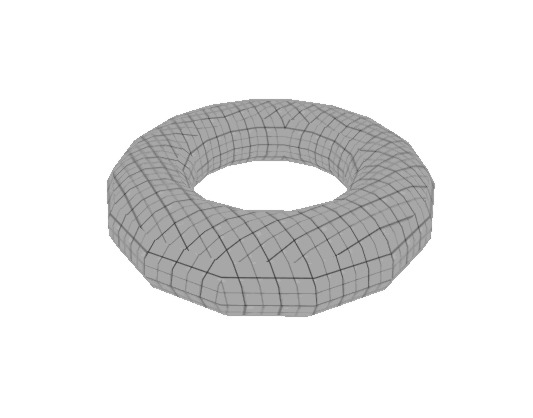
====Torus==== | |||
[[ | The torus resembles an inner tube or a donut. This primitive can easily mass polygons so keep the number of faces on this primitive low. Like the arch it has a special [[Hammer Torus Properties | Tool]]. | ||
[[Image:primitive_torus.jpg]] | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 11 October 2006
Primitive types
A primitive is by definition a very simple structure. Primitive, as it relates to the Valve Hammer Editor, refers to a brush-based object that conforms to a common shape. Primitives include arches, blocks, cylinders, spheres, spikes, tori and wedges. Some are made up of multiple brushes but are still considered primitive as they are used commonly and are of a simple shape. Two examples of multiple-brush primitives are tori and arches.
Simple
Block
The block, a basic cube, is the most used object when mapping in Hammer.
Cylinder
A cylindrical brush created with a specified number of sides.
Sphere
The sphere is a rather complicated piece of geometry, so it would be wise to be careful with the number of faces you give the sphere.
Spike
Like the cylinder, but all the top vertices come to 1 central point.
Wedge
The wedge is basically a triangular prism.
Complex
Arch
This creates a basic arch as defined by the Arch Tool. Multiple blocks slightly rotated will be created within 1 group.
Torus
The torus resembles an inner tube or a donut. This primitive can easily mass polygons so keep the number of faces on this primitive low. Like the arch it has a special Tool.