Eyeball: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
 Tip:An iris material can cover the entire surface of the eye if need be.
Tip:An iris material can cover the entire surface of the eye if need be.
 Tip:The
Tip:The
(Added some more info to the points. Feels like the first paragraph should be moved to its own "Eyes" shader page, as this isn't how EyeRefract works, and may cause confusion as we only talk about the qc part here!) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
: The bone which the eye is parented to, typically the head. | : The bone which the eye is parented to, typically the head. | ||
;<code><X> <Y> <Z></code> | ;<code><X> <Y> <Z></code> | ||
: World location of the center of the ball of the eye. | : World location of the center of the ball of the eye. While your eye doesn't need to be a sphere in the model, Source will always map the material according to an invisible ball. | ||
;<code><material_name></code> | ;<code><material_name></code> | ||
: Material above which the iris material will be drawn. Make sure every eye has a unique one! | : Material above which the iris material will be drawn. Make sure every eye has a unique one! You can either use a material with the <code>[[Eyes]]</code> shader, or the <code>[[EyeRefract]]</code> shader, but the latter is pretty much always recommended due to its more accurate rendering methods and more parameters to mess with. | ||
;<code><diameter></code> | ;<code><diameter></code> | ||
: Width of the eyeball when viewed from the front. Used to prevent the iris from rolling inside the head. {{note|The iris will travel in a circle even if the eyeball is oval. Your model's [[flex]] should accommodate for this.}} | : Width of the eyeball when viewed from the front. Used to prevent the iris from rolling inside the head. {{note|The iris will travel in a circle even if the eyeball is oval. Your model's [[flex]] should accommodate for this. {{todo|How?}} }} | ||
;<code><angle></code> | ;<code><angle></code> | ||
: Default yaw offset (from directly forward) for iris. Humans are typically 2-4 degrees [[Wikipedia:Strabismus|wall-eyed]]. Not setting this correctly will result in either your characters appearing cross-eyed, or if you've compensated by misplacing the ball of the eye, them not tracking side to side. | : Default yaw offset (from directly forward) for iris. Humans are typically 2-4 degrees [[Wikipedia:Strabismus|wall-eyed]]. Not setting this correctly will result in either your characters appearing cross-eyed, or if you've compensated by misplacing the ball of the eye, them not tracking side to side. Should be a negative value for the left eye, and a positive value for the right eye. | ||
;<code><iris_material></code> | ;<code><iris_material></code> | ||
: Material used as the iris texture. (This property is deprecated) | : Material used as the iris texture. (This property is deprecated) | ||
;<code><iris_scale></code> | ;<code><iris_scale></code> | ||
: Scale of the iris texture. | : Scale of the iris texture. The model's UV map does not influence the eye material in any way. {{todo|While this is true for <code>[[EyeRefract]]</code>, is this also true for the <code>[[Eyes]]</code> shader?}} | ||
=== Example === | === Example === | ||
Revision as of 04:25, 26 January 2019
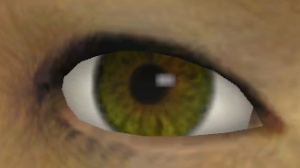
Eyeball is a property of $model. It consists of two components:
- An 'eye white' surface on the model, with a unique material.
- A dynamic iris decal that travels over the eye white material to simulate the eye looking in different directions.
Parameters
qc_eyes tool can help you manage the potentially confusing string of numbers needed for this command.<name>- Name of eyeball, used to match eyelid rules. For humans, use
righteyeandlefteye. <bone_name>- The bone which the eye is parented to, typically the head.
<X> <Y> <Z>- World location of the center of the ball of the eye. While your eye doesn't need to be a sphere in the model, Source will always map the material according to an invisible ball.
<material_name>- Material above which the iris material will be drawn. Make sure every eye has a unique one! You can either use a material with the
Eyesshader, or theEyeRefractshader, but the latter is pretty much always recommended due to its more accurate rendering methods and more parameters to mess with. <diameter>- Width of the eyeball when viewed from the front. Used to prevent the iris from rolling inside the head.
 Note:The iris will travel in a circle even if the eyeball is oval. Your model's flex should accommodate for this. Todo: How?
Note:The iris will travel in a circle even if the eyeball is oval. Your model's flex should accommodate for this. Todo: How? <angle>- Default yaw offset (from directly forward) for iris. Humans are typically 2-4 degrees wall-eyed. Not setting this correctly will result in either your characters appearing cross-eyed, or if you've compensated by misplacing the ball of the eye, them not tracking side to side. Should be a negative value for the left eye, and a positive value for the right eye.
<iris_material>- Material used as the iris texture. (This property is deprecated)
<iris_scale>- Scale of the iris texture. The model's UV map does not influence the eye material in any way. Todo: While this is true for
EyeRefract, is this also true for theEyesshader?
Example
Hover your mouse over each value for its description.
$model "female_01" "female_01_reference_RE.smd" { eyeball righteye ValveBiped.Bip01_Head1 -1.261 -3.702 64.974 eyeball_r 1 4 pupil_r 0.66 }
See also
- The
EyeRefractandEyesshaders - Eye Position Setup, for a guide to calculating the various numbers required
qc_eyes, a tool to aid your calculations