Spawn(): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
 Warning:
Warning:
 Tip:
Tip:
TomEdwards (talk | contribs) (created) |
Thunder4ik (talk | contribs) m (→top: Unicodifying, replaced: [[Image: → [[File:) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | {{lang|Spawn()}} | ||
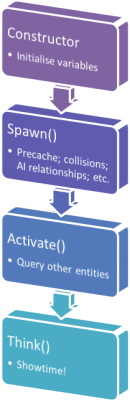
[[File:Entity init.png|right|130px|The Source engine entity initialisation process.]] | |||
'''<code>Spawn()</code>''' is a <code>void</code> member function of <code>[[CBaseEntity]]</code> that is available through inheritance to every entity in a Source game. It is called by the engine whenever a new instance of an entity is created, much like a constructor. | '''<code>Spawn()</code>''' is a <code>void</code> member function of <code>[[CBaseEntity]]</code> that is available through inheritance to every entity in a Source game. It is called by the engine whenever a new instance of an entity is created, much like a constructor. Some base classes execute code from it, so to be safe always call <code>BaseClass::Spawn()</code> from your version. | ||
Spawn() is used to perform tasks that must take place before the entity can enter the world, typically including calling <code>[[Precache()]]</code> and <code>[[SetSolid()]]</code>, initialising [[VPhysics]] simulation and setting up global AI parameters | <code>Spawn()</code> is used to perform tasks that must take place before the entity can enter the world, typically including calling <code>[[Precache()]]</code> and <code>[[SetSolid()]]</code>, initialising [[VPhysics]] simulation and setting up global AI parameters. | ||
{{warning|<code>Spawn()</code> is called '''immediately''' after the creation of the entity. If this has occurred during level load there is no guarantee that other entities have been spawned yet unless they are spawned by the | Variable initialisation should be performed in the [[Wikipedia:Constructor (object-oriented programming)|class constructor]] rather than <code>Spawn()</code> to avoid overwriting data from the map's entity block. | ||
{{warning|<code>Spawn()</code> is called '''immediately''' after the creation of the entity. If this has occurred during level load there is no guarantee that other entities have been spawned yet (unless they are spawned by the entity itself). Therefore, any code which requires the entity to search or otherwise link itself to other entities is usually unreliable. Use <code>[[Activate()]]</code> for these tasks, which is called after all spawning has completed.}} | |||
{{tip|<code>[[CBasePlayer]]::Spawn()</code> is called when the player respawns, too. Use <code>InitialSpawn()</code> for code that should only run once.}} | |||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
<source lang="cpp"> | |||
void CNPC_Antlion::Spawn() | |||
{ | |||
Precache(); | |||
SetHullType( HULL_MEDIUM ); | |||
SetHullSizeNormal(); | |||
SetDefaultEyeOffset(); | |||
SetNavType( NAV_GROUND ); | |||
SetSolid( SOLID_BBOX ); | |||
AddSolidFlags( FSOLID_NOT_STANDABLE ); | |||
SetMoveType( MOVETYPE_STEP ); | |||
... | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| Line 32: | Line 38: | ||
*[[Activate()]] | *[[Activate()]] | ||
*[[Think()]] | *[[Think()]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Your First Entity]] | ||
[[Category:Functions]] | [[Category:Functions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:17, 6 January 2024
Spawn() is a void member function of CBaseEntity that is available through inheritance to every entity in a Source game. It is called by the engine whenever a new instance of an entity is created, much like a constructor. Some base classes execute code from it, so to be safe always call BaseClass::Spawn() from your version.
Spawn() is used to perform tasks that must take place before the entity can enter the world, typically including calling Precache() and SetSolid(), initialising VPhysics simulation and setting up global AI parameters.
Variable initialisation should be performed in the class constructor rather than Spawn() to avoid overwriting data from the map's entity block.
Spawn() is called immediately after the creation of the entity. If this has occurred during level load there is no guarantee that other entities have been spawned yet (unless they are spawned by the entity itself). Therefore, any code which requires the entity to search or otherwise link itself to other entities is usually unreliable. Use Activate() for these tasks, which is called after all spawning has completed.CBasePlayer::Spawn() is called when the player respawns, too. Use InitialSpawn() for code that should only run once.Example
void CNPC_Antlion::Spawn()
{
Precache();
SetHullType( HULL_MEDIUM );
SetHullSizeNormal();
SetDefaultEyeOffset();
SetNavType( NAV_GROUND );
SetSolid( SOLID_BBOX );
AddSolidFlags( FSOLID_NOT_STANDABLE );
SetMoveType( MOVETYPE_STEP );
...
}